Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A carrier of a genetic disorder who does not show symptoms is most likely to be
__________ to transmit it to offspring.
a. | homozygous for the trait and unable | b. | homozygous for the trait and
able | c. | heterozygous for the trait and able | d. | heterozygous for the trait and
unable | e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Many genetic disorders of humans are caused by
a. | drinking during pregnancy. | b. | recessive alleles. | c. | a mutation that
occurs in the egg, sperm, or zygote that gives rise to the affected individual. | d. | multiple
alleles. | e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
3.
|
The vast majority of people afflicted with recessive disorders are born to
parents who were
a. | not affected at all by the disease. | b. | subjected to some environmental toxin that
caused the disease in their children. | c. | slightly affected by the disease, showing some
but not all of the symptoms. | d. | both affected by the
disease. | e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Crossing over __________ genes into assortments of __________ not found in the
parents.
a. | combines unlinked . . . alleles | b. | recombines linked . . .
alleles | c. | combines linked . . . genes | d. | recombines unlinked . . .
genes | e. | recombines unlinked . . . chromosomes |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following is/are recessive sex-linked human conditions?
a. | red-green color blindness | b. | hemophilia | c. | muscular
dystrophy | d. | All of the choices are correct. | e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Why are sex-linked conditions more common in men than in women?
a. | Women simply do not develop the disease regardless of their genetic
composition. | b. | The sex chromosomes are more active in men than in women. | c. | Men acquire two
copies of the defective gene during fertilization. | d. | Men need to inherit only one copy of the
recessive allele for the condition to be fully expressed. | e. | None of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The monomers of DNA and RNA are
a. | nucleic acids. | b. | amino acids. | c. | nucleotides. | d. | monosaccharides. | e. | fatty
acids. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which one of the following is false?
a. | DNA molecules have a sugar-phosphate backbone. | b. | DNA uses the sugar
deoxyribose. | c. | DNA uses the nitrogenous base uracil. | d. | DNA is a nucleic acid. | e. | One DNA molecule can
include four different nucleotides in its structure. |
|
|
|
9.
|
DNA replication
a. | occurs by the addition of nucleotides to the end of the DNA
molecule. | b. | uses each strand of a DNA molecule as a template for the creation of a new
strand. | c. | produces two daughter DNA molecules that are complementary to each
other. | d. | results in the formation of four new DNA strands. | e. | begins when two DNA
molecules join together to exchange segments. |
|
|
|
10.
|
If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be
a. | GCCTAG. | b. | GCCAUC. | c. | GCCATG. | d. | TAACGT. | e. | CGGTAC. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The copying mechanism of DNA is most like
a. | using a photographic negative to make a positive image. | b. | threading beads onto
a string. | c. | carving a figure out of wood. | d. | joining together links to make a
chain. | e. | mixing flour, sugar, and water to make bread dough. |
|
|
|
12.
|
When one DNA molecule is copied to make two DNA molecules, the new DNA
contains
a. | 75% of the parent DNA. | b. | 50% of the parent DNA. | c. | none of the parent
DNA. | d. | 100% of the parent DNA. | e. | 25% of the parent
DNA. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which one of the following sequences best describes the flow of information when
a gene directs the synthesis of a cellular component?
a. | DNA --> tRNA --> mRNA --> protein | b. | RNA --> DNA
--> RNA --> protein | c. | protein -->RNA -->DNA | d. | DNA --> RNA
--> protein | e. | DNA --> amino acid --> RNA --> protein |
|
|
|
14.
|
If you commit a crime, you need to make sure that you do not leave even the
smallest speck of blood, hair, etc., from your body behind because if you do, the DNA in this
material can be amplified by __________, subjected to genetic analysis, and used to identify you as
the perpetrator of the crime.
a. | blotting | b. | PCR | c. | RFLP | d. | reverse transcriptase | e. | ATP |
|
|
|
15.
|
The polymerase chain reaction relies upon unusual, heat-resistant __________
that were isolated from bacteria living in hot springs.
a. | mRNA | b. | phages | c. | plasmids | d. | restriction enzymes | e. | DNA polymerase
molecules |
|
|
|
16.
|
A change in the relative frequencies of alleles in the gene pool of a population
is called
a. | diversifying selection. | b. | microevolution. | c. | genetic
drift. | d. | directional selection. | e. | mutation. |
|
|
|
17.
|
In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, homozygous dominant individuals in a population
are represented by
a. | 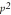 . . | b. | 2pq. | c. | 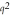 . . | d. | q or p. | e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Fitness increases when an organism
a. | lives for a long time. | b. | survives many hardships. | c. | is stronger than the
other organisms in its community. | d. | passes on a greater proportion of its genes to
the next generation. | e. | is
disease-free. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Cells with two sets of genetic information are described by the term
a. | polyploid. | b. | diploid. | c. | triploid. | d. | haploid. | e. | tetraploid. |
|
|
|
Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
|
|
|
20.
|
The entire process represented here can be called:
a. | gene expression. | b. | gene regulation. | c. | DNA
replication. | d. | DNA mutation. | e. | Transformation. |
|
|
|
21.
|
This molecule is made of amino acids.
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | Both (1) and (2) | e. | Both (2) and
(3) |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on the diagram below:
|
|
|
22.
|
Chromatin is found in which stage?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 4 | e. | DNA is diffused into
chromatin in all stages. |
|
|
|
The next two questions refer to the following diagram. 1, 3, and 5 refer
to the actual structure represented by the diagram. 2 and 4 refer to the event/stage
represented by the arrow.
|
|
|
23.
|
Process (4) is:
a. | Interphase. | b. | Metaphase. | c. | Anaphase. | d. | Telophase. | e. | Meiosis. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on this graph and images: The
following graph was created using data collected through the “Natural Selection” done in
class. The “beans” used to simulate the prey population are diagramed
below.
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Genetic diversity within the population is an important component of natural
selection; genetic diversity in the “prey” population is represented by the different
types of beans used. | b. | Darker color (black and brown) seems to be more
of an adaptation in this simulation compared to smaller size (black and spotted). | c. | If this simulation
is continued for 10 more generations, the resulting population will have less genetic diversity
compared to the initial population. | d. | Genetic variation will not
“recover” in this simulation because we cannot simulate random mutations and genetic
recombination due to sexual reproduction. | e. | The black phenotype has the highest associated
fitness. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which would be the most appropriate title for this graph (what is the data
actually showing)?
a. | Change in phenotypic frequency in prey population due to natural
selection. | b. | Change in allele frequency in prey population due to natural
selection. | c. | Percentage of each phenotype remaining after each generation. | d. | Survival of the
fittest due to natural selection. | e. | The Bean Lab. |
|
|
|
The following four diagrams show the structures of different molecules.
Answer the following questions based on your ability to identify them.
|
|
|
26.
|
Which molecule, when broken down into its monomers, is consumed in the
glycolysis pathway?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 4 | e. | Both (2) and
(3) |
|
|
|
Using diagrams below answer the following questions. 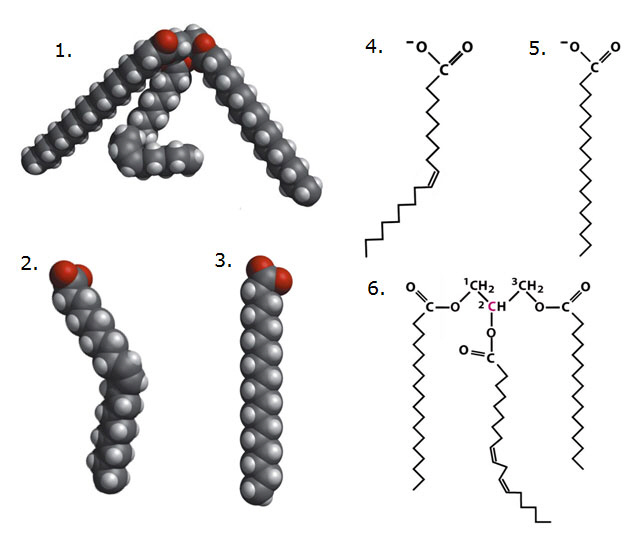
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the above diagrams show an unsaturated fat?
a. | 1, 4, 5, 6 | b. | 2, 3, 1 | c. | 1, 2, 6,
4 | d. | 5, 3, 1 | e. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
Using the diagram answer the following questions. 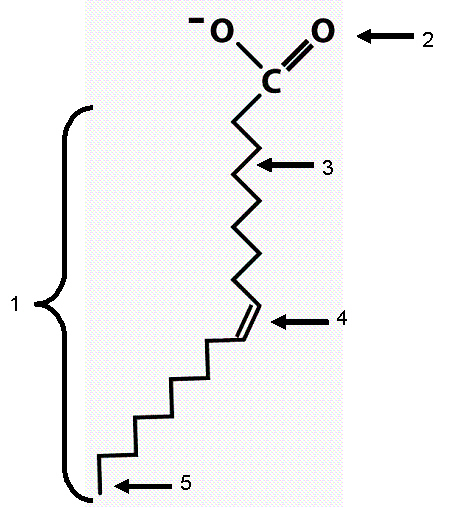
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following terms best describes this molecule?
a. | fatty acid | b. | saturated fatty acid | c. | polypeptide | d. | phospholipid | e. | triglyceride |
|
|
|
29.
|
Diploid organisms
a. | have corresponding alleles on homologous chromosomes. | b. | are usually the
result of the fusion of two haploid gametes. | c. | have two sets of
chromosomes. | d. | have pairs of homologous chromosomes. | e. | all of these |
|
|
|
30.
|
If short hair (S) is dominant to long hair (s), animals SS
and Ss have the same
a. | parents. | b. | genotypes. | c. | phenotypes. | d. | alleles. | e. | genes. |
|