Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which are NOT macromolecules?
a. | proteins | b. | starches | c. | nucleotides | d. | lipids | e. | nucleic
acids |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which compound would most likely be characterized as hydrophobic?
a. | ethyl alcohol | b. | simple sugar | c. | cholesterol | d. | glycerol | e. | amino
acid |
|
|
|
3.
|
Nucleotides are the building blocks for
a. | proteins. | b. | steroids. | c. | lipids. | d. | RNA, NAD+, and
FAD. | e. | carbohydrates. |
|
|
|
4.
|
The breakdown of large molecules by the enzymatic addition of water is an
example of what kind of reaction?
a. | oxidation | b. | reduction | c. | condensation | d. | hydrolysis | e. | none of the
above. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which reaction results in the breakdown of a chemical into smaller
substances?
a. | synthesis | b. | hydrolysis | c. | condensation | d. | polymerization | e. | both hydrolysis and
condensation |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which is NOT a monosaccharide?
a. | glucose | b. | fructose | c. | deoxyribose | d. | starch | e. | ribose |
|
|
|
7.
|
Cellulose is
a. | a material found in cell walls. | b. | formed using products of
photosynthesis. | c. | a plant protein. | d. | a component of cell
membranes. | e. | both (a) and (b) above. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The bonds linking amino acids to form the primary structure of a protein can be
characterized as:
a. | peptide | b. | covalent | c. | ionic | d. | disulfide | e. | both (a) and (b)
above |
|
|
|
9.
|
The relative impermeability of membranes to water-soluble molecules is a result
of the
a. | nonpolar nature of water molecules. | b. | presence of large proteins that extend through
both sides of membranes. | c. | large pores that allow molecules to freely move
across the membrane. | d. | presence of cellulose and other polar molecules
in the membranes. | e. | characteristics of the phospholipids in the
lipid bilayer. |
|
|
|
The diagrams below are representations of the protein-hormone insulin. The
protein insulin is made up of two polypeptides referred to as “A chain” and “B
chain”. The two chains are clearly labeled on each of the three representations
below.
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | The insulin protein’s secondary structure contains alpha
helices. | b. | The diagrams above highlight an example (or examples) of tertiary
structure. | c. | The region labeled (1) highlights a part of insulin’s primary
structure. | d. | Both (a) and (b) are true. | e. | All of the above are
true. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | The insulin displayed above is made up of a total of 51 amino
acids. | b. | The interaction labeled (2) is a peptide bond. | c. | The structure
labeled (3) is a specific type of tertiary interaction. | d. | Both (a) and (b) are
true. | e. | All of the above are true. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | The “A chain” of insulin is made up of 21 amino acids and has
alpha-helical secondary structure. | b. | The two chains of insulin are held together by
peptide bonds. | c. | The “B chain” of insulin has a single 5’ end a single 3’
end. | d. | Both (a) and (b) are true. | e. | All of the above are
true. |
|
|
|
13.
|
A hydrogen bond is
a. | a sharing of a pair of electrons between a hydrogen and an oxygen
nucleus. | b. | a sharing of a pair of electrons between a hydrogen nucleus and either an oxygen or a
nitrogen nucleus. | c. | an attractive force that involves a hydrogen
atom and an oxygen or a nitrogen atom that are either in two different molecules or within the same
molecule. | d. | none of these | e. | all of these |
|
|
|
14.
|
Glucose dissolves in water because it
a. | ionizes. | b. | is a polysaccharide. | c. | is polar and forms
many hydrogen bonds with the water molecules. | d. | has a very reactive primary
structure. | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
15.
|
The secondary structure of proteins can be
a. | helical. | b. | sheetlike. | c. | globular. | d. | the sequence of amino
acids. | e. | both helical and sheetlike. |
|
|
|
16.
|
The nucleotide most closely associated with energy is
a. | cyclic AMP. | b. | FAD. | c. | NAD. | d. | ATP. | e. | all of
these |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following are lipids?
a. | steroids | b. | triglycerides | c. | oils | d. | waxes | e. | all of
these |
|
|
|
The following four diagrams show different orientations of five water
molecules. Note that the diagrams vary in water molecule orientation and partial charges on the
atoms. Study the diagrams carefully and answer the following questions.
|
|
|
18.
|
The interaction between individual water molecules:
a. | are weak interactions between opposite partial charges. | b. | break when
temperature is increased. | c. | are covalent bonds. | d. | both (a) and (b)
above. | e. | all answers are correct. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The chemical bonds holding the single oxygen and two hydrogen atoms together in
a single water molecule are ______ bonds and the bonds between multiple water molecules are _____
bonds.
a. | strong ionic..... weak hydrogen | b. | strong covalent.....weak hydrogen
| c. | weak covalent..... strong hydrogen | d. | strong covalent.....strong
hydrogen | e. | strong ionic.... weak covalent |
|
|
|
The following four diagrams show the structures of different molecules.
Answer the following questions based on your ability to identify them.
|
|
|
20.
|
Which macromolecule is characterized as being hydrophobic?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | All molecules here
are hydrophobic. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which diagram shows a structural isomer of cellulose?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | None of the
above. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which macromolecule is best associated with the terms saturated and
unsaturated?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | All molecules have
saturated and unsaturated structures. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following choices has the above images associated with the correct
term?
a. | 1....glycosidic linkage | b. | 2....polysacharride | c. | 3....peptide
bond | d. | 4....peptide bond | e. | 1....tertiary structure or sidechain
interactions. |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows a sequence of a reaction. The numbers 1through
4 identify different parts of the overall structure.
|
|
|
24.
|
Numbers 1-4 highlight different parts of the structures show in the
diagram. Which part is directly involved in the tertiary interactions (tertiary structure) that
determine the three dimensional structure of this macromolecule?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | Both (1) and
(2) |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following correctly identifies the region of the protein shown in
the diagram above that is specifically involved in creating the interactions that form secondary
structural motifs such alpha helixes and beta sheets?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 4 | d. | 1 and 4 | e. | 1 and
3 |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows the different levels of structure for a type of
macromolecule. Answer the questions based on your understanding of how these structures are
maintained.
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following levels of structure is most likely NOT to be
affected by high temperature, changes in salt concentration, and changes in pH?
|
|
|
27.
|
Which image represents the interaction of multiple polypeptides to form a
functional protein?
|
|
|
Protein Structure: Using the following diagram correctly answer the following
questions. 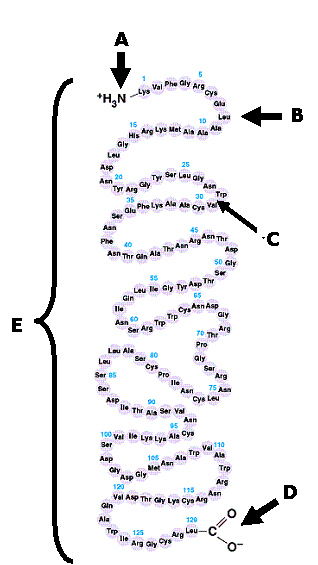
|
|
|
28.
|
The region labeled C is best (or most specifically) described as
a. | an R group or side chain | b. | a covalent bond between two amino
acids | c. | a beta sheet | d. | a secondary structure | e. | a tertiary
interaction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the choices correctly identifies only examples of tertiary
structure in the above diagram?
a. | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | b. | 1, 3, 5 | c. | 1, 2
,4 | d. | 3 only | e. | 3, 4, 5 |
|
|
|
Using diagrams below answer the following questions. 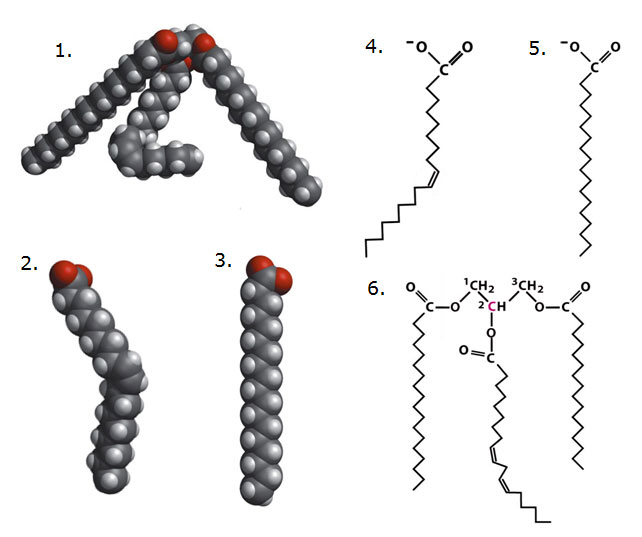
|
|
|
30.
|
Correctly pair the molecules in the diagrams above.
a. | 4.....5 | b. | 1.....4 and 5 | c. | 2.....4 | d. | 3.....5 | e. | both c and d are
correctly paired |
|
|
|
31.
|
Using the diagrams above correctly identify a trigyceride.
a. | 1 and 6 are both trigyclerides | b. | 1 is a phospholipid | c. | 6 is
phospholipid | d. | 4 is a triglyceride | e. | 3 is a
triglyceride |
|
|
|
Identify the diagram below and answer the following questions.
|
|
|
32.
|
“The predicted nature of the labeled area _____ is _____ due to
_____.” Which of the following accurately complete this statement?
a. | 1... polar... due to the large phosphate group with multiple oxygen
atoms. | b. | 2... nonpolar... the large number of C-H bonds that tend to share electrons
evenly. | c. | 4... hydrophilic... double bonds within the fatty acid tail. | d. | Both (a) and
(b) | e. | All of the above. |
|
|
|
The two images below both show the structure of the cell membrane composed of
two layers of phospholipids. Recall the chemical characteristics of a phospholipid and its role
in the function of the membrane. The labels (numbers 1 through 5) for the two diagrams
correspond to the same “part” of the two diagrams.
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the labeled regions identifies a single phospholipid molecule?
|
|
|
34.
|
What are you actually referring to when using the term “lipid
bilayer”?
|
|
|
Figure 1 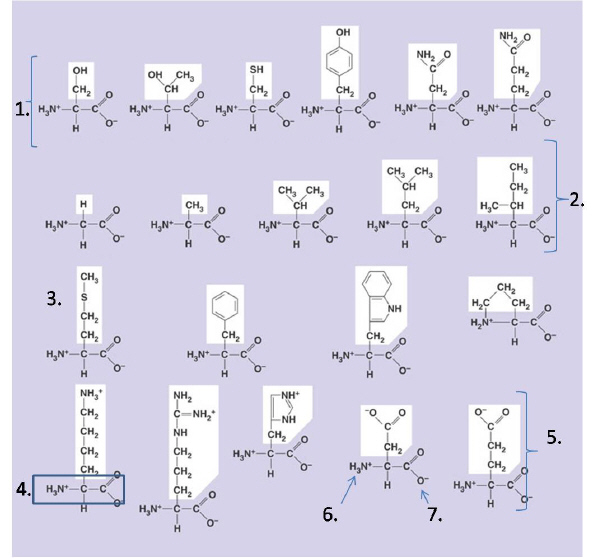
|
|
|
35.
|
Assuming all residues shown are part of a polypeptide chain, compare the amino
acids labeled 1, 2, and 5. Which of the following is a correct observation regarding these
amino acids?
a. | 1 is the only polar sidechain whereas the other sidechains are strongly
non-polar | b. | 1 and 2 are hydrophillic and 3 and 5 are hydrophobic | c. | 1 and 5 will
interact with an aqueous environment whereas 2 will not | d. | All the sidechains
are hydrophillic | e. | none of the above choices are correct |
|
|
|
Figure 2: Molecules Essential for Life 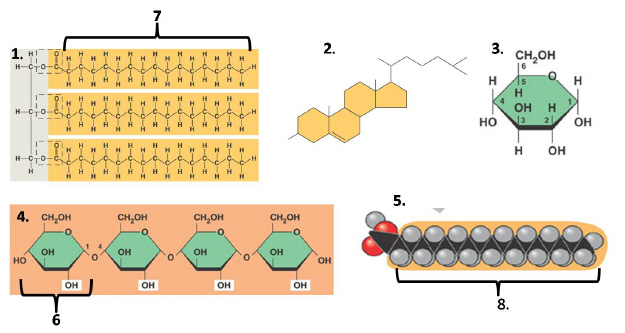
|
|
|
36.
|
Which of the following diagrams are correctly linked in the answers
below:
a. | 1, 2, 5 are all members of the macromolecules group known as
lipids | b. | 2, 3, 4 are all members of the carbohydrate macromolecule group | c. | 4 and 5 are members
of the protein macromolecule group | d. | 3, 4, and 5 are members of the lipid
macromolecule group | e. | none of the above are completely
correct |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following is correctly pairs the possible monomer unit (or
monomer-like unit) to the polymer (or polymer-like unit)?
a. | 7 is the monomer unit to 2 | b. | 2 is the monomer unit to 7 | c. | 3 is the monomer
unit of 4 | d. | 5 is monomer-like unit of 1 | e. | both c and d are
true |
|
|
|
Figure 5-Lysosyme 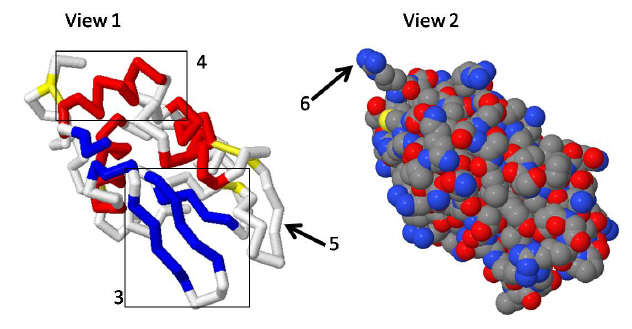
|
|
|
38.
|
The above views of the protein Lyzozyme shows the protein in two different ways.
Which statement best explains the differences within the views.
a. | View 1 shows the details of the primary sequence of the protein whereas View 2 only
shows the backbone of the polypeptide | b. | View 1 and 2 are showing the exact same
information | c. | View 1 shows the secondary structure of a protein whereas view 2 shows the globular,
spacefill view of the protein. | d. | View 1 shows the sidechains that are in the
active site of the protein whereas view 2 shows only tertiary and structure | e. | all of the above are
correct |
|
|
|
39.
|
Areas highlighted by 4 and 5 ---.
a. | are examples of secondary structure | b. | are examples of tertiary
structure | c. | are examples of quarternary sturcture | d. | are examples of primary
structure | e. | both a and d are correct |
|
|
|
40.
|
Compare the information conveyed through the are labeled 5 and the area labeled
6.
Which of the following statements are correct?
a. | Area 6 shows a sidechain | b. | Area 5 shows several
sidechains | c. | Area 6 shows only backbone | d. | Area 5 shows only backbone | e. | a and d are
correct |
|