Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The primitive earth's atmosphere did NOT contain
a. | water vapor. | b. | free nitrogen. | c. | free
hydrogen. | d. | free oxygen. | e. | inert gases. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Eukaryotic cells spend most of their cell cycle in which phase?
a. | anaphase | b. | interphase | c. | prophase | d. | metaphase | e. | telophase |
|
|
|
3.
|
A person with AB blood illustrates the principle of
a. | pleiotropy. | b. | incomplete dominance. | c. | blending
inheritance. | d. | codominance. | e. | polygenic
inheritance. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Genes located close together on the same chromosomes are referred to as
__________ genes and generally __________.
a. | linked . . . do not sort independently during meiosis | b. | associated . . .
sort independently during meiosis | c. | homologous . . . are inherited
together | d. | linked . . . sort independently during meiosis | e. | codependent . . . do
not sort independently during meiosis |
|
|
|
5.
|
Crossing over __________ genes into assortments of __________ not found in the
parents.
a. | combines unlinked . . . alleles | b. | recombines linked . . .
alleles | c. | combines linked . . . genes | d. | recombines unlinked . . .
genes | e. | recombines unlinked . . . chromosomes |
|
|
|
6.
|
How many sex chromosomes are in a human gamete?
a. | four | b. | five | c. | three | d. | one | e. | two |
|
|
|
7.
|
Any gene located on a sex chromosome
a. | will exhibit pleiotropy. | b. | is called a sex-linked
gene. | c. | will exhibit codominance. | d. | is called a recessive gene. | e. | is called a dominant
allele. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following is/are recessive sex-linked human conditions?
a. | red-green color blindness | b. | hemophilia | c. | muscular
dystrophy | d. | All of the choices are correct. | e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Why are sex-linked conditions more common in men than in women?
a. | Women simply do not develop the disease regardless of their genetic
composition. | b. | The sex chromosomes are more active in men than in women. | c. | Men acquire two
copies of the defective gene during fertilization. | d. | Men need to inherit only one copy of the
recessive allele for the condition to be fully expressed. | e. | None of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
10.
|
If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be
a. | GCCTAG. | b. | GCCAUC. | c. | GCCATG. | d. | TAACGT. | e. | CGGTAC. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The directions for each amino acid in a polypeptide are indicated by a codon
that consists of __________ nucleotide(s) in an RNA molecule.
|
|
|
12.
|
If you commit a crime, you need to make sure that you do not leave even the
smallest speck of blood, hair, etc., from your body behind because if you do, the DNA in this
material can be amplified by __________, subjected to genetic analysis, and used to identify you as
the perpetrator of the crime.
a. | blotting | b. | PCR | c. | RFLP | d. | reverse transcriptase | e. | ATP |
|
|
|
13.
|
The polymerase chain reaction relies upon unusual, heat-resistant __________
that were isolated from bacteria living in hot springs.
a. | mRNA | b. | phages | c. | plasmids | d. | restriction enzymes | e. | DNA polymerase
molecules |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following constitutes a basic, modern definition of a sexually
reproducing species?
a. | a group of individuals who resemble each other, on average, more than they resemble
anything else | b. | the smallest unit that can engage in microevolution | c. | a group of
populations whose members can interbreed and produce fertile offspring | d. | a group of
individuals who interbreed | e. | a group of individuals living in the same place
at the same time |
|
|
|
15.
|
A population is
a. | a collection of communities. | b. | a group of individuals of different species
living in the same place at the same time. | c. | the smallest unit that can
evolve. | d. | applicable only to animals that reproduce asexually. | e. | All of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
16.
|
A change in the relative frequencies of alleles in the gene pool of a population
is called
a. | diversifying selection. | b. | microevolution. | c. | genetic
drift. | d. | directional selection. | e. | mutation. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Fitness increases when an organism
a. | lives for a long time. | b. | survives many hardships. | c. | is stronger than the
other organisms in its community. | d. | passes on a greater proportion of its genes to
the next generation. | e. | is
disease-free. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Gel electrophoresis
a. | separates fragments of DNA based on their net charge | b. | separates fragments
of DNA based on their base pair size | c. | separates fragments of DNA based on their net
weight | d. | Both (b) and (c) are correct | e. | All above choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The distribution of cytoplasm to daughter cells is accomplished during
a. | prokaryotic fission. | b. | mitosis. | c. | meiosis. | d. | cytokinesis (cytoplasmic
division). | e. | karyokinesis. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Although mitosis divides a cell into two, the original number of chromosomes is
maintained because
a. | the cells become haploid | b. | the chromosomes are replicated before
division | c. | the chromosomes are replicated during division | d. | the DNA molecules
are split into smaller pieces | e. | the double stranded DNA becomes single
stranded |
|
|
|
Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
|
|
|
21.
|
The entire process represented here can be called:
a. | gene expression. | b. | gene regulation. | c. | DNA
replication. | d. | DNA mutation. | e. | Transformation. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on the diagram below:
|
|
|
22.
|
Chromatin is found in which stage?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 4 | e. | DNA is diffused into
chromatin in all stages. |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows a cross section of a plant root tip. Answer
the questions based on your ability to identify the stage of the cell cycle the cells are in. 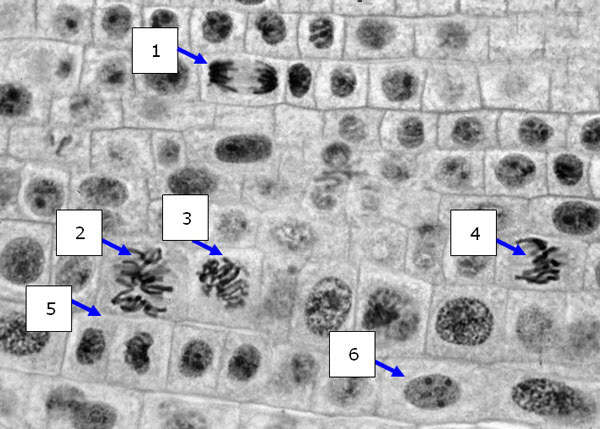
|
|
|
23.
|
Which cell is most likely to be in interphase?
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on this graph and images: The
following graph was created using data collected through the “Natural Selection” done in
class. The “beans” used to simulate the prey population are diagramed
below.
|
|
|
24.
|
Which would be the most appropriate title for this graph (what is the data
actually showing)?
a. | Change in phenotypic frequency in prey population due to natural
selection. | b. | Change in allele frequency in prey population due to natural
selection. | c. | Percentage of each phenotype remaining after each generation. | d. | Survival of the
fittest due to natural selection. | e. | The Bean Lab. |
|
|
|
The following four diagrams show the structures of different molecules.
Answer the following questions based on your ability to identify them.
|
|
|
25.
|
Which diagram represents the monomer units of proteins?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | Both (2) and
(4) |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which macromolecule is characterized as being hydrophobic?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | All molecules here
are hydrophobic. |
|
|
|
Using diagrams below answer the following questions. 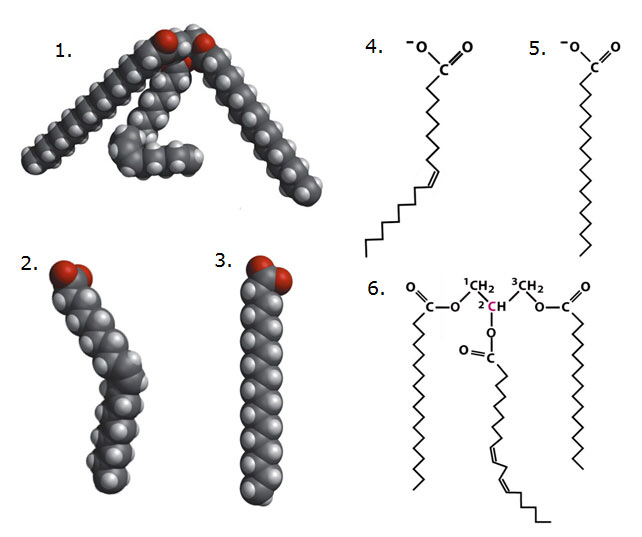
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the above diagrams show an unsaturated fat?
a. | 1, 4, 5, 6 | b. | 2, 3, 1 | c. | 1, 2, 6,
4 | d. | 5, 3, 1 | e. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
28.
|
If R is dominant to r, the offspring of the cross of RR
with rr will
a. | be homozygous. | b. | display the same phenotype as the RR
parent. | c. | display the same phenotype as the rr parent. | d. | have the same
genotype as the RR parent. | e. | have the same genotype as the rr
parent. |
|
|
|
29.
|
If short hair (S) is dominant to long hair (s), animals SS
and Ss have the same
a. | parents. | b. | genotypes. | c. | phenotypes. | d. | alleles. | e. | genes. |
|
|
|
Observe the following diagram and answer the following
questions. 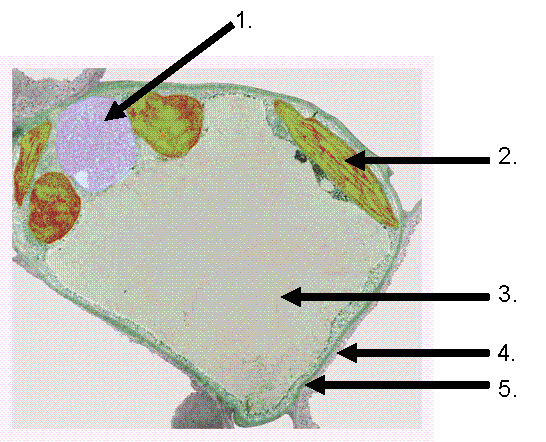
|
|
|
30.
|
Which structure(s) identified above is (are) unique only to plant cells?
a. | 1 | b. | 1.....2 | c. | 1.....2.....3 | d. | 2.....3.....4 | e. | 1.....2.....3.....4.....5. |
|