Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
The following diagram shows one end of a replication bubble. Labels
“1” through “6” point at separate objects. “7” and
“8” point at the two separate strands of the molecule. Answer the following
questions based on your understanding of replication and this diagram.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which statement is true?
a. | The enzyme labeled “1” breaks covalent bonds to separate the double
stranded DNA. | b. | The enzyme labeled “2” adds DNA nucleotides to the 5’ end of the
new, extending strand of DNA. | c. | “4” is the promoter
sequence. | d. | “7” points at the 3’ end of DNA. | e. | The enzyme labeled
“3” creates RNA primers necessary for DNA polymerase. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The two, newly synthesized, DNA molecules at the replication fork can be
described as the “leading” and “lagging” strands. Which of the
following statements is false?
a. | The top strand is the leading strand. | b. | The leading strand must be created in multiple
fragments that are later connected by the enzyme ligase. | c. | Starting at the
origin of replication, the leading strand requires a single RNA primer. | d. | Both (a) and (b) are
false. | e. | Both (b) and (c) are false. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on the diagram below:
|
|
|
3.
|
Order the stages of the cell cycle correctly.
a. | 1, 4, 3, 2. | b. | 1, 2, 4, 3. | c. | 1, 3, 4,
2. | d. | 4, 1, 2, 3. | e. | 4, 3, 1, 2. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Chromatin is found in which stage?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 4 | e. | DNA is diffused into
chromatin in all stages. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which stage is characterized by the condensing of DNA into chromosomes and the
breakdown of the nuclear membrane?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 4 | e. | None of the
above. |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows a cross section of a plant root tip. Answer
the questions based on your ability to identify the stage of the cell cycle the cells are in. 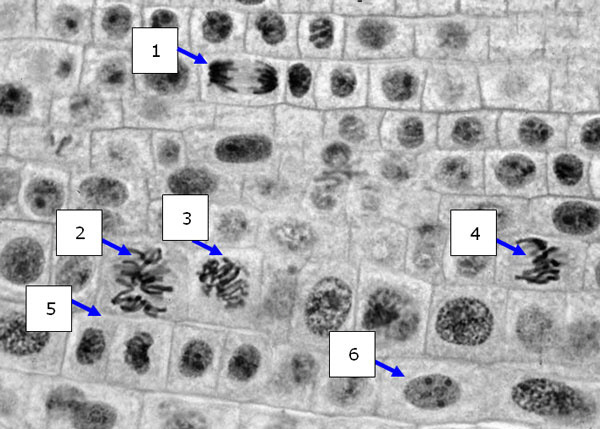
|
|
|
6.
|
Which cell is most likely to be in interphase?
|
|
|
7.
|
Which cell no longer contains DNA organized as sister chromatids?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 4 | e. | All of the
above. |
|
|
|
The next two questions refer to the following diagram. 1, 3, and 5 refer
to the actual structure represented by the diagram. 2 and 4 refer to the event/stage
represented by the arrow.
|
|
|
8.
|
DNA replication occurs:
a. | Before structure (1) forms. | b. | During process (2). | c. | During
interphase. | d. | Both (a) and (c). | e. | Both (b) and
(c). |
|
|
|
9.
|
Diagram (3) represents:
a. | centromeres. | b. | chromatin. | c. | a single molecule of
DNA. | d. | two molecules of DNA that are exact copies of each other. | e. | homologous
chromosomes. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Process (4) is:
a. | Interphase. | b. | Metaphase. | c. | Anaphase. | d. | Telophase. | e. | Meiosis. |
|
|
|
The following graph tracks the amount of DNA in a single nucleus through the
cell cycle. Answer the questions based on the graph.
|
|
|
11.
|
Stages I, II, and III are part of:
a. | Interphase | b. | Prophase | c. | Metaphase | d. | Mitosis | e. | Meiosis |
|
|
|
12.
|
Sister chromatids are found in which of the following stages?
a. | I | b. | V | c. | VI | d. | VII | e. | Both (I) and
(V) |
|
|
|
The following graph tracks the amount of DNA in a single nucleus through the
process of meiosis. Answer the questions based on the graph.
|
|
|
13.
|
Meiosis I is which group of the following stages?
a. | I, II, III | b. | IV, V, VI, VII | c. | VIII, IX, X,
XI | d. | I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII | e. | None of the above
combinations |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Tetrads form during IV. | b. | Cells are diploid during
IV. | c. | Cells are diploid during XII. | d. | DNA is replicated once during this
process. | e. | The cell divides twice during this process. |
|
|
|
15.
|
During which stage is the amount of DNA in the cell characterized as 1n?
a. | I | b. | IV | c. | VII | d. | XII | e. | None of the
above. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on your understanding of the events going
on in the cell diagramed below.
|
|
|
16.
|
Which statement is false?
a. | n=2. | b. | There are two tetrads in the
diagram. | c. | Crossing over may be occurring during this stage. | d. | This diagram
represents a stage of mitosis. | e. | There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes
in the diagram. |
|
|
|
17.
|
This diagram shows a cell during a stage of cell division. This type of
division accomplishes which of the following:
a. | Creates gametes. | b. | “Shuffles” genetic material from
the individual to create genetically unique daughter cells. | c. | Reduces chromosome
number to half that of other cells in the body. | d. | Both (a) and (b) | e. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on this diagram:
|
|
|
18.
|
Which statement is true?
a. | The karyotype was taken from a male. | b. | The karyotype shows 22
chromosomes. | c. | The karyotype belongs to an individual with trisomy 21. | d. | The DNA shown here
must have been taken from a cell in interphase. | e. | Each chromosome is made up of multiple
molecules of DNA. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The cause of the above disorder is most likely:
a. | Genetic mutations in DNA sequence. | b. | Cells’ inability to complete cytokinesis
after mitosis. | c. | Nondisjunction during meiosis. | d. | Nondisjunction during
mitosis. | e. | Caused by an toxin that interrupts the regulation of the cell
cycle. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which statement regarding normal human karyotype and human chromosomes is
false?
a. | There are 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes. | b. | There are a total of
46 molecules of DNA. | c. | The karyotype shows a diploid number of
chromosomes. | d. | The karyotype shows DNA molecules that are condensed. | e. | There are 46
homologous pairs of chromosomes in a human. |
|
|
|
21.
|
In mitosis, if a parent cell
has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes?
|
|
|
22.
|
Cells two sets of genetic
information are described by the term
a. | polyploid. |
b. | diploid. |
c. | triploid. |
d. | haploid. |
e. | tetraploid. |
|
|
|
23.
|
If a parent cell has 16
chromosomes and undergoes meiosis, the resulting cells will have how many
chromosomes?
|
|
|
24.
|
Homologous
chromosomes
a. | may exchange parts during
meiosis. |
b. | have alleles for the same characteristics even though the gene expression may not
be
the same. |
c. | are in pairs, one chromosome of each pair from the father
and one from the mother. |
d. | pair up during meiosis. |
e. | all of these |
|
|
|
25.
|
Crossing over is one of the
most important events in meiosis because
a. | it produces new arrays of alleles on
chromosomes. |
b. | homologous chromosomes must be separated into different daughter
cells. |
c. | the number of chromosomes allotted to each daughter cell must be
halved. |
d. | homologous chromatids must be separated into different daughter
cells. |
e. | all of these |
|
|
|
26.
|
The appropriate adjective to
describe DNA replication is
a. | nondisruptive. |
b. | semiconservative. |
c. | progressive. |
d. | natural. |
e. | lytic. |
|
|
|
27.
|
DNA
polymerase
a. | is an
enzyme. |
b. | adds new nucleotides to a strand. |
c. | proofreads DNA strands to see that they are
correct. |
d. | derives energy from ATP for synthesis of DNA strands. |
e. | all of these |
|
|
|
28.
|
You are the director of
research for a drug company. A list of candidate drugs is brought to you. Which of the
following shows the greatest promise as a cancer chemotherapy agent? A drug that
a. | prevents tetrad
formation. |
b. | prevents crossing over. |
c. | prevents sister chromatids from separating at
anaphase. |
d. | causes cells to divide at a right angle from their usual
orientation. |
e. | interferes with cellular
respiration. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Two chromosomes in a nucleus
that carry loci for the same traits in the same positions on the chromosome but specify different
versions of some traits constitute a pair of
a. | complementary
chromosomes. |
b. | homologous chromosomes. |
c. | polyploid chromosomes. |
d. | heterologous
chromosomes. |
e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Nondisjunction occurs
when
a. | a portion of a chromosome breaks off
and is lost. |
b. | two chromosomes fuse into one. |
c. | members of a chromosome pair fail to
separate. |
d. | chromosomes replicate too many times. |
e. | an entire pair of chromosomes is lost during meiosis
I. |
|