|
|
|
1.
|
The transfer of a (one) phosphate group from one molecule to another molecule or
compound (such as one ADP) is called
a. | carbon fixation. | b. | ionization. | c. | hydrogen
bonding. | d. | hydrogenation. | e. | substrate level
phosphorylation. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following statements about ATP is true?
a. | ATP can be produced in a stage of photosynthesis. | b. | ATP is generated
through the breakdown of organic compounds such as glucose. | c. | ATP is generated
through anaerobic respiration. | d. | ATP is generated through aerobic
respiration. | e. | all of the statements are correct. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Anything that prevents ATP formation will most likely
a. | force the cell to rely on lipids for energy. | b. | result in the
conversion of kinetic energy to potential energy. | c. | force the cell to rely on ADP for
energy. | d. | have no effect on the cell. | e. | result in cell
death. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Respiration __________, and cellular respiration __________.
a. | is gas exchange . . . produces ATP | b. | uses glucose . . . produces
glucose | c. | produces glucose . . . is gas exchange | d. | produces ATP . . . is gas
exchange | e. | produces glucose . . . produces oxygen |
|
|
|
5.
|
When molecules are broken apart in cellular respiration
a. | the heat produced is used to drive biological reactions. | b. | the oxygen released
from the compounds that are broken apart is always used as an energy source. | c. | the energy released
in the reactions is eventually channeled into molecules of ATP, mostly through oxidative
phosphorylation. | d. | ATP is converted into ADP. | e. | ADP is released as a waste
product. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which pathway releases (yields) the most energy from organic molecules in the
form of ATP?
a. | aerobic respiration | b. | anaerobic respiration | c. | alcoholic
fermentation | d. | lactate fermentation | e. | All release the same amount, but through
different means. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which one of the following statements is false? Cellular
respiration
a. | is a single chemical reaction with just one step that directly yields
ATP. | b. | releases heat. | c. | produces water. | d. | produces carbon
dioxide. | e. | consumes glucose. |
|
|
|
8.
|
How do cells capture the energy released by cellular respiration?
a. | The energy is transferred to oxygen as the final electron
acceptor. | b. | Cell transfer the energy to the bonds of ATP. | c. | They store it in
molecules of carbon dioxide. | d. | They produce glucose. | e. | None of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following are products of cellular
respiration?
a. | glucose and carbon dioxide | b. | oxygen and carbon dioxide | c. | energy to make ATP
and carbon dioxide | d. | oxygen and energy to make
ATP | e. | oxygen and glucose |
|
|
|
10.
|
The overall equation for the cellular respiration of glucose is
a. | 6 CO2 + 6 H2O --> C6H12O6 +
6 O2 + energy. | b. | C6H12O12 + 6
CO2 --> 6 O2 + 6 H2O + energy. | c. | C3H12O6 + 6 H2O --> 5
CO2 + 6 O2 + energy. | d. | C6H12O6+ 6
O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy. | e. | None of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of stages in cellular
respiration?
a. | the Krebs cycle, pyruvate oxidation, ETC-oxidative phosphorylation, and
glycolysis | b. | ETC-oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate oxidation, the Krebs cycle, and
glycolysis | c. | ETC-oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate oxidation, glycolysis, and the Krebs
cycle | d. | glycolysis, ETC-oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate oxidation, and the Krebs
cycle | e. | glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the Krebs cycle, and ETC-oxidative
phosphorylation |
|
|
|
12.
|
Glycolysis
a. | occurs in the mitochondria. | b. | is the final step of cellular
respiration. | c. | results in the production of pyruvate. | d. | occurs in the cytoplasm. | e. | both (c) and (d)
above are true. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following is a result of glycolysis?
a. | conversion of NADH to NAD+ | b. | a net loss of two ATPs per glucose
molecule | c. | conversion of glucose to two 3-carbon compounds | d. | production of
CO2 | e. | conversion of FAD to FADH2 |
|
|
|
14.
|
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle are located in the
a. | intermembrane space of the mitochondrion. | b. | outer mitochondrial
membrane. | c. | inner mitochondrial membrane. | d. | mitochondrial matrix. | e. | cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
15.
|
During the ETC and oxidative phosphorylation,
a. | ATP is synthesized when H+ ions move down a concentration gradient through ATP
synthase. | b. | Glucose is broken down and CO2 is released. | c. | Energy is released
as H+ ions move freely across mitochondrial membranes. | d. | A concentration gradient is generated when
large numbers of H+ ions are passively transported from the matrix of the mitochondrion to the
mitochondrion's intermembrane space. | e. | Oxygen provides high energy electrons to power
the active transport of H+ ions across the inner membrane. |
|
|
|
16.
|
A drug is tested in the laboratory and is found to create holes in both
mitochondrial membranes. Scientists suspect that the drug will be harmful to human cells because it
will inhibit
a. | the fermentation pathways that will produce NAD+ for glycolysis to continue in
anaerobic conditions.. | b. | glycolysis from hydrolyzing
glucose. | c. | the formation of alcohol. | d. | the Krebs cycle that will produce NADH
necessary for the ETC. | e. | the establishment of hydrogen ion gradients
across the inner mitochondrial membrane. |
|
|
|
17.
|
In the electron transport chain of cell respiration, the final electron acceptor
is
a. | ATP. | b. | a molecule of carbon
dioxide. | c. | an oxygen atom. | d. | a molecule of water. | e. | ADP. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The term anaerobic means
a. | without CO2. | b. | without ATP. | c. | without
O2. | d. | with O2. | e. | without
bacteria. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Under anaerobic conditions muscle cells produce
a. | ethyl alcohol (ethanol) | b. | oxygen. | c. | pyruvate. | d. | lactate (lactic acid). | e. | citrate. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which one of the following metabolic reactions is common in both
the aerobic and anaerobic pathways?
a. | chemiosmosis | b. | glycolysis | c. | ETC | d. | the Krebs cycle | e. | None of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The summary equation for photosynthesis is
a. | the same as the equation for glycolysis written in reverse. | b. | 6 CO2 + 6
H2O + sunlight+ chlorophyll --> C6H12O6 + 6
O2. | c. | 6 O2 + 6 H2O + sunlight+ chlorophyll -->
C6H12O6 + 6 CO2. | d. | C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + sunlight --> 5
CO2 + 6 H2O. | e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which one of the following statements is false?
a. | Photosynthesis produces O2; respiration produces
CO2. | b. | The principal electron carrier in photosynthesis is NADPH; the principal electron
carrier in respiration is NADH. | c. | Photosynthesis is ultimately powered by light
energy; respiration is powered by the chemical energy of food molecules being broken
down. | d. | ATP is not produced during photosynthesis. ATP is only produced during
respiration. | e. | Photosynthesis consumes CO2; respiration consumes
O2. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Chloroplasts contain disk-like membranous sacs arranged in stacks called
a. | cristae. | b. | thylakoids. | c. | grana. | d. | stroma. | e. | vacuoles. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Where is chlorophyll found in a plant cell?
a. | cristae | b. | cytoplasm | c. | stroma | d. | matrix | e. | thylakoid
membranes |
|
|
|
25.
|
The oxygen released into the air as a product of photosynthesis comes from
a. | chlorophyll. | b. | carbon dioxide. | c. | water. | d. | glucose. | e. | None of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which statement regarding photosynthesis is false?
a. | Photosynthesis is divided into the light-dependent and light-independent
reactions. | b. | Photosynthesis functions to convert light energy into chemical energy stored in ATP
which is then used to use carbon dioxide to build carbohydrates. | c. | Photosynthesis is
the only mechanism available to plants to make ATP. | d. | Photosynthesis involves the fixation of carbon
dioxide from the air. | e. | Photosynthesis relies on converting solar
energy into energy stored in ATP and NADPH to drive the light-independent
reactions. |
|
|
|
27.
|
The light-dependent reactions occur in the __________ while the
light-independent (dark) reactions occurs in the __________.
a. | stroma . . . thylakoid membranes | b. | stroma . . . nucleus | c. | cytoplasm . . .
stroma | d. | thylakoid membranes . . . stroma | e. | cytoplasm . . . thylakoid
membrane |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which statement regarding the light-dependent reactions is false?
a. | photons are absorbed by chlorophyll | b. | water is split to release
electrons | c. | oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport
chain. | d. | ATP and NADPH are produced. | e. | The final electron acceptor, NADPH, carries
high-energy electrons to be used in the light-independent reactions. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following are produced during the light reactions of
photosynthesis?
a. | ATP, NADPH, O2 | b. | ATP, NADPH, CO2 | c. | glucose, ADP, NADP+,
CO2 | d. | ADP, NADP+, O2 | e. | glucose, ADP,
NADP+ |
|
|
|
30.
|
ATP and NADPH in the chloroplast
a. | are produced in associated with events taking place on the inner mitochondrial
membrane. | b. | are inputs to the light-dependent reactions. | c. | provide the chemical
energy necessary to plants to form glucose. | d. | are used by the mitochondria to produce more
ATP. | e. | All of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Carbon fixation
a. | occurs when carbon and oxygen from CO2 are incorporated into a large,
high-energy, organic molecule. | b. | provides the cell with a supply of NADPH
molecules. | c. | is facilitated by enzymes in the mitochondria. | d. | powers the process
of glucose synthesis by supplying the cell with ATP. | e. | occurs during the light
reactions. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which one of the following is true?
a. | Photosynthesis occurs in mitochondria and cellular respiration occurs in
chloroplasts. | b. | Cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria and in chloroplasts. | c. | Photosynthesis
occurs in mitochondria and in chloroplasts. | d. | Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts and
cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria. | e. | Neither cellular respiration nor photosynthesis
occurs in mitochondria and in chloroplasts. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Mitochondria transfer _____ energy from _____ to ATP; chloroplasts transform
_____ energy into the chemical energy of ATP.
a. | food . . . light . . . nuclear | b. | light . . . food . . .
kinetic | c. | food . . . light . . . chemical | d. | chemical . . . food . . .
light | e. | nuclear . . . light . . . food |
|
|
|
|
34.
|
Use the following diagram to answer the next questions.
The above diagram shows a. all macromolecules are capable of being
broken down in order to form ATP.
b. all macromolecules are
converted into glucose in order to go through cellular
respiration
c. cellular respiration takes in only
glucose.
d. other macromolecules are are capable of entering cell
respiration at intermediates.
e. a and d are true
|
|
|
35.
|
Use the following diagram to answer the next questions.
The above diagram shows a
pathway that occurs when: a. fats are
broken down to make ATP.
b. oxygen is available to a human
cell.
c. oxygen is deficient in a human
cell.
d. carbon dioxide is not
available.
e. more ATP than what is produced through aerobic
respiration is needed.
|
|
|
36.
|
Use the following diagram to answer the next questions. This is a diagram
of a reaction taking place in the mitochondria.
Which letter represents a
molecule that provides the energy required to establish a high concentration of ions in the
intermembrane space? a.
1.
b. 2.
c.
4.
d. 5.
e. 7.
|
|
|
37.
|
Without this molecule, the cell will be forced to switch ATP production to
anaerobic respiration. a.
1.
b. 2.
c.
4.
d. 5.
e. 7.
|
|
|
38.
|
The membrane seen in this diagram is the: a. cell
membrane
b. thylakoid membrane
c.
nuclear membrane
d. outer mitochondrial
membrane
e. inner mitochondrial membrane
|
|
|
39.
|
The next two questions refer to the following diagram: 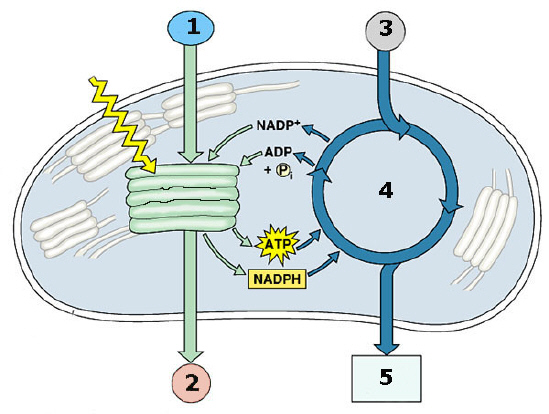 This molecule is "fixed" together to make glucose, which can be then used
for the synthesis of more complex carbohydrates and other organic molecules. a. 1.
b.
2.
c. 3.
d.
5.
e. both (2) and (3) above
|
|
|
40.
|
This molecule is released as a byproduct of the light reactions and is necessary
for the plants to be able to release ATP from glucose when light is not available: a. 1.
b.
2.
c. 3.
d.
5.
e. none of the above.
|