Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The phenotypic ratio resulting
from a dihybrid cross showing independent assortment is expected to be
a. | 9:1:1:3. |
b. | 1:2:1. |
c. | 3:1. |
d. | 9:3:3:1. |
e. | 3:9:9:1. |
|
|
|
2.
|
A carrier of a genetic disorder
who does not show symptoms is most likely to be __________ to transmit it to
offspring.
a. | homozygous for the trait and
unable |
b. | homozygous for the trait and able |
c. | heterozygous for the trait and
able |
d. | heterozygous for the trait and unable |
e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Dr. Smith's parents have
normal hearing. However, Dr. Smith has an inherited form of deafness. Deafness is a recessive trait
that is associated with the abnormal allele d. The normal allele at this locus, associated with normal hearing, is D.
Dr. Smith's parents could have which of the following genotypes?
a. | dd and dd |
b. | DD and dd |
c. | DD
and DD |
d. | Dd
and Dd |
e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Imagine that beak color in a
finch species is controlled by a single gene. You mate a finch homozygous for orange (pigmented) beak
with a finch homozygous for ivory (unpigmented) beak and get numerous offspring, all of which have a
pale, ivory-orange beak. This pattern of color
expression is most likely to be an example of
a. | pleiotropy. |
b. | crossing over. |
c. | codominance. |
d. | polygenic inheritance. |
e. | incomplete
dominance. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The expression of both alleles
for a trait in a heterozygous individual illustrates
a. | blending
inheritance. |
b. | incomplete dominance. |
c. | polygenic inheritance. |
d. | pleiotropy. |
e. | codominance. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Genes located close together on
the same chromosomes are referred to as __________ genes and generally
__________.
a. | linked . . . do not sort
independently during meiosis |
b. | associated . . . sort independently during
meiosis |
c. | homologous . . . are inherited together |
d. | linked . . . sort independently during
meiosis |
e. | codependent . . . do not sort independently during
meiosis |
|
|
|
7.
|
Crossing over __________ genes
into assortments of __________ not found in the parents.
a. | combines unlinked . . .
alleles |
b. | recombines linked . . . alleles |
c. | combines linked . . .
genes |
d. | recombines unlinked . . . genes |
e. | recombines unlinked . . .
chromosomes |
|
|
|
8.
|
What is the normal complement
of sex chromosomes in a human male?
a. | two Y chromosomes |
b. | one Y chromosome |
c. | two X
chromosomes and one Y chromosome |
d. | two X
chromosomes |
e. | one X
chromosome and one Y chromosome |
|
|
|
9.
|
Any gene located on a sex
chromosome
a. | will exhibit
pleiotropy. |
b. | is called a sex-linked
gene. |
c. | will exhibit codominance. |
d. | is called a recessive
gene. |
e. | is called a dominant allele. |
|
|
|
Use the picture below to answer the questions that follow 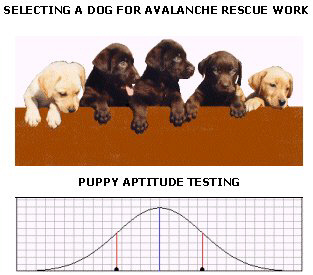
|
|
|
10.
|
The bell
curve diagram shown above is typical of which type of inheritance pattern?
a. | incomplete
dominance |
b. | dominant/recessive inheritance |
c. | sex-linked inheritance |
d. | heterozygote advantage |
e. | polygenic
inheritance |
|
|
|
11.
|
A locus is
a. | a recessive gene. | b. | an unmatched allele. | c. | a sex
chromosome. | d. | the location of an allele on a chromosome. | e. | a dominant
gene. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Hybrid organisms produced from a cross between two pure-breeding organisms
belong to which generation?
|
|
|
13.
|
If short hair (L) is dominant to long hair (l), animals LL
and Ll have the same
a. | parents. | b. | genotypes. | c. | phenotypes. | d. | alleles. | e. | genes. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Short hair (L) is dominant to long hair (l). If a short-haired
animal of unknown origin is crossed with a long-haired animal and they produce one long-haired and
one short-haired offspring, this would indicate that
a. | the short-haired animal was pure-breeding. | b. | the short-haired
animal was not pure-breeding. | c. | the long-haired animal was not
pure-breeding. | d. | the long-haired animal was pure-breeding. | e. | none of these can be
determined with two offspring |
|
|
|
15.
|
For monohybrid experiments, a testcross could result in which of the following
ratios?
a. | 1:1 | b. | 2:1 | c. | 9:3:3:1 | d. | 1:2:1 | e. | 3:1 |
|
|
|
16.
|
An individual with a genotype of Aa Bb CC is able to produce how many
different kinds of gametes?
|
|
|
17.
|
In cocker spaniels, black coat color (B) is dominant over red (b),
and solid color (S) is dominant over spotted (s). If two dihybrids (Bb Ss) were
crossed, the most common phenotype would be
a. | black and solid. | b. | black and spotted. | c. | red and
solid. | d. | red and spotted. | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
18.
|
In cocker spaniels, black coat color (B) is dominant over red (b),
and solid color (S) is dominant over spotted (s). A cross of Bb Ss with bb
ss would produce the phenotypic ratio
a. | 9:3:3:1. | b. | 1:1:1:1. | c. | 1:2:1. | d. | 3:1. | e. | none of
these |
|
|
|
19.
|
Coat color in one breed of mice is controlled by incompletely dominant alleles
so that yellow and white are homozygous, while cream is heterozygous. The cross of two cream
individuals will produce
a. | all cream offspring. | b. | equal numbers of white and yellow mice, but no
cream. | c. | equal numbers of white and cream mice. | d. | equal numbers of yellow and cream
mice. | e. | equal numbers of white and yellow mice, with twice as many creams as the other two
colors. |
|
|
|
20.
|
If a child belonged to blood type O, he or she could not have been produced by
which set of parents?
a. | Type A mother and type B father | b. | Type A mother and type O
father | c. | Type AB mother and type O father | d. | Type O mother and type O
father |
|
|
|
21.
|
A gene that produces multiple effects is called
a. | a multiple allele. | b. | an autosome. | c. | an epistatic
gene. | d. | a pleiotropic gene. | e. | an incompletely dominant
gene. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Genes are
a. | located on chromosomes. | b. | inherited in the same way as
chromosomes. | c. | arranged in linear sequence on chromosomes. | d. | assorted
independently during meiosis. | e. | all of these |
|
|
|
23.
|
DNA coding regions that affect the same trait are called
a. | homologues. | b. | alleles. | c. | autosomes. | d. | loci. | e. | gametes. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following designates a normal human female?
|
|
|
25.
|
If alleles L, M, and N are on the maternal chromosome and
l, m, and n are on the paternal chromosome, the only way that a gamete from a
heterozygote will produce a gamete with alleles l, m, and N is through
a. | nondisjunction. | b. | the laws of segregation. | c. | the law of
independent assortment. | d. | crossing over. | e. | chromosome
aberration. |
|
|
|
26.
|
A colorblind man and a woman with normal vision whose father was colorblind have
a son. Colorblindness, in this case, is caused by an X-linked recessive gene. If only the male
offspring are considered, the probability that their son is colorblind is
a. | .25 (or 25 percent). | b. | .50 (or 50 percent). | c. | .75 (or 75
percent). | d. | 1.00 (or 100 percent). |
|
|
|
27.
|
An X-linked carrier is a
a. | homozygous dominant female. | b. | heterozygous female. | c. | homozygous recessive
female. | d. | homozygous male. | e. | heterozygous
male. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Nondisjunction involving the X chromosomes may occur during oogenesis and
produce two kinds of eggs. If normal sperm fertilize these two types, which of the following pairs of
genotypes are possible?
a. | XX and XY | b. | XXY and XO | c. | XYY and
XO | d. | XYY and YO | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
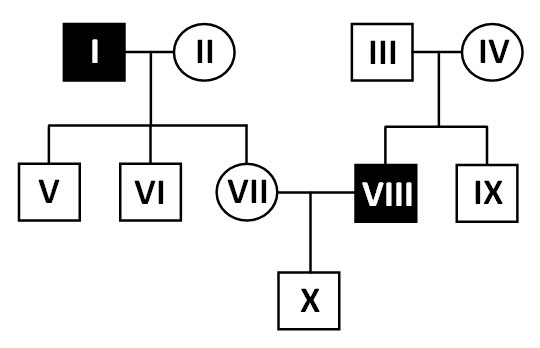
The following pedigree shows
the inheritance of an autosomal genetic disorder inherited in simple Mendelian patterns.
|
|
|
29.
|
Determine if the genetic
disorder is dominant or recessive. Which individual can possibly be a NON-carrier of the allele causing the
disorder.
a. | III |
b. | V |
c. | IX |
d. | X |
e. | All individuals above must have at least one copy of the affected
allele. |
|
|
|
30.
|
If (X) marries a woman that has
the same genetic disorder his father had, what is the probability that his child will also have the
disease?
a. | 0% |
b. | 50% |
c. | 66.7% |
d. | 75% |
e. | 100% |
|