Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Propanol and isopropanol are isomers. This means that they have
a. | the same molecular formula but different chemical properties. | b. | the same molecular
formula, but propanol is the liquid form of the compound and isopropanol is the gaseous
form. | c. | different molecular formulas but the same chemical properties. | d. | the same molecular
formula and the same chemical properties. | e. | the same number of carbon atoms but different
numbers of oxygen and hydrogen atoms. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which one of the following statements about the monomers and polymers found in
living organisms is false?
a. | Monomers are joined together by the process of hydrolysis. | b. | Monomers serve as
building blocks for polymers. | c. | The monomers used to make polymers are
essentially universal. | d. | Cells typically make all of their
macromolecules from a set of 40-50 common monomers and a few other ingredients that are
rare. | e. | DNA is built from just four kinds of monomers. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which list below consists of only polymers?
a. | sugars, amino acids, nucleic acids, lipids | b. | proteins, lipids,
nucleic acids, polysaccharides | c. | proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, amino
acids | d. | polysaccharides, lipids, amino acids, nucleic acids | e. | proteins, lipids,
nucleotides, sugars |
|
|
|
4.
|
A molecule with the formula 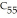 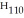 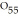 is probably a(n) a. | protein. | b. | oil. | c. | steroid. | d. | polysaccharide. | e. | wax. |
|
|
|
5.
|
A disaccharide forms when
a. | two starches join by hydrolysis. | b. | two starches join by dehydration
synthesis. | c. | two monosaccharides join by dehydration synthesis. | d. | a starch and a
monosaccharide join by dehydration synthesis. | e. | two monosaccharides join by
hydrolysis. |
|
|
|
6.
|
The storage form of carbohydrates in animals is __________ and in plants is
__________.
a. | glycogen . . . starch | b. | starch . . . glycogen | c. | sucrose . . .
glycogen | d. | cellulose . . . glycogen | e. | glycogen . . .
cellulose |
|
|
|
7.
|
A triglyceride
a. | is a type of fat. | b. | consists of three fatty acids attached to a
glycerol. | c. | is hydrophobic. | d. | plays a role in energy
storage. | e. | All of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Fatty acids with double bonds between some of their carbons are said to
be
a. | unsaturated. | b. | triglycerides. | c. | monoglycerides. | d. | saturated. | e. | completely
hydrogenated. |
|
|
|
9.
|
A phospholipid is composed of
a. | one glycerol molecule linked to three phosphate groups. | b. | one glycerol
molecule linked to three fatty acids. | c. | one fatty acid molecule linked to one glycerol
molecule and two phosphate groups. | d. | one fatty acid molecule linked to three
glycerol molecules. | e. | one glycerol molecule linked to one phosphate
group and two fatty acids. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Nucleotides
a. | contain nitrogenous bases. | b. | contain phosphate groups. | c. | contain sugar
molecules. | d. | can be linked together to form nucleic acids. | e. | All of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
11.
|
A new "wonder food" is being distributed by a rival company. The
researchers in your company determine that the "wonder food" contains only carbon, oxygen,
and hydrogen. At this point, your researchers can say with certainty that the food
a. | could only be made of carbohydrates. | b. | includes proteins. | c. | could only be made
of triglycerides. | d. | does not include proteins or nucleic
acids. | e. | includes nucleic acids. |
|
|
|
The following four diagrams show different orientations of five water
molecules. Note that the diagrams vary in water molecule orientation and partial charges on the
atoms. Study the diagrams carefully and answer the following questions.
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the above four diagrams show the correct orientation of water molecules
interacting as a liquid?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | Both (1) and (4) are
possible orientations. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The interaction between individual water molecules:
a. | are weak interactions between opposite partial charges. | b. | break when
temperature is increased. | c. | are covalent bonds. | d. | both (a) and (b)
above. | e. | all answers are correct. |
|
|
|
14.
|
The chemical bonds holding the single oxygen and two hydrogen atoms together in
a single water molecule are ______ bonds and the bonds between multiple water molecules are _____
bonds.
a. | strong ionic..... weak hydrogen | b. | strong covalent.....weak hydrogen
| c. | weak covalent..... strong hydrogen | d. | strong covalent.....strong
hydrogen | e. | strong ionic.... weak covalent |
|
|
|
The following four diagrams show the structures of different molecules.
Answer the following questions based on your ability to identify them.
|
|
|
15.
|
Which diagram represents the monomer units of proteins?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | Both (2) and
(4) |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which macromolecule is best associated with the terms saturated and
unsaturated?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | All molecules have
saturated and unsaturated structures. |
|
|
|
17.
|
in diagram 4, the “R” represents the:
a. | amino group. | b. | carboxyl group. | c. | enzyme. | d. | active site. | e. | sidechain. |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows a sequence of a reaction. The numbers 1through
4 identify different parts of the overall structure.
|
|
|
18.
|
Numbers 1-4 highlight different parts of the structures show in the
diagram. Which part is directly involved in the tertiary interactions (tertiary structure) that
determine the three dimensional structure of this macromolecule?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | Both (1) and
(2) |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is true about the “backbone” of this
molecule?
a. | Highlighted by “1”. | b. | Highlighted by
“2”. | c. | Contains carbons and nitrogens. | d. | Contains carbons, nitrogens, and
sulfurs. | e. | Both (b) and (c). |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows the different levels of structure for a type of
macromolecule. Answer the questions based on your understanding of how these structures are
maintained.
|
|
|
20.
|
Which diagram above, 1-5, represents an alpha-helix, a type of secondary
structure?
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following levels of structure is most likely NOT to be
affected by high temperature, changes in salt concentration, and changes in pH?
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on the diagram below:
|
|
|
22.
|
This diagram shows a:
a. | Dehydration synthesis reaction. | b. | hydrolysis reaction. | c. | Formation of a
peptide bond. | d. | Both (a) and (c) above. | e. | None of the
above. |
|
|
|
23.
|
What molecule should be identified in place of (3)?
a. | Inhibitor. | b. | Enzyme. | c. | Water. | d. | Inhibitors. | e. | None of the
above. |
|
|
|
The two images below both show the structure of the cell membrane composed of
two layers of phospholipids. Recall the chemical characteristics of a phospholipid and its role
in the function of the membrane. The labels (numbers 1 through 5) for the two diagrams
correspond to the same “part” of the two diagrams.
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the labeled regions identifies a single phospholipid molecule?
|
|
|
25.
|
What are you actually referring to when using the term “lipid
bilayer”?
|
|
|
The diagram below shows a transmembrane protein (a protein embedded in the lipid
bilayer) that acts as a channel to transport molecules across the membrane. You should recognize the
parts of the lipid bilayer by comparing them to an earlier question which shows the membrane in the
same view. The boxed area highlights details of the protein chain that sits in the
membrane. Each “R” represents a separate sidechain and is labeled 1 through
5. Answer the following questions based on your understanding of the structure and
characteristics of amino acids, proteins, and the lipid bilayer.
|
|
|
26.
|
This protein exhibits secondary structure characteristics called:
a. | backbones. | b. | hydrophilic. | c. | beta
sheets. | d. | alpha helices. | e. | disulfide
bonds. |
|
|
|
27.
|
The sidechains labeled 4 and 5 can possibly belong to which of the following
amino acids?
a. | Aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and valine. | b. | Alanine, glycine,
and proline. | c. | Asparagine, glutamine, and threonine. | d. | Both (a) and (b) above. | e. | None of the
above. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following statements must be true about the amino acid
sidechain labeled 1?
a. | This sidechain must have similar chemical characteristics to that of fatty acid
chains. | b. | This sidechain must be able to interact with nonpolar molecules. | c. | This sidechain must
be able to interact with water. | d. | Both (a) and (b) above can be
true. | e. | Both (a) and (c) above can be true. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the choices correctly identifies only examples of tertiary
structure in the above diagram?
a. | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | b. | 1, 3, 5 | c. | 1, 2
,4 | d. | 3 only | e. | 3, 4, 5 |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the above interaction could be characterized as an hydrophobic
interaction?
|
|
|
Using diagrams below answer the following questions. 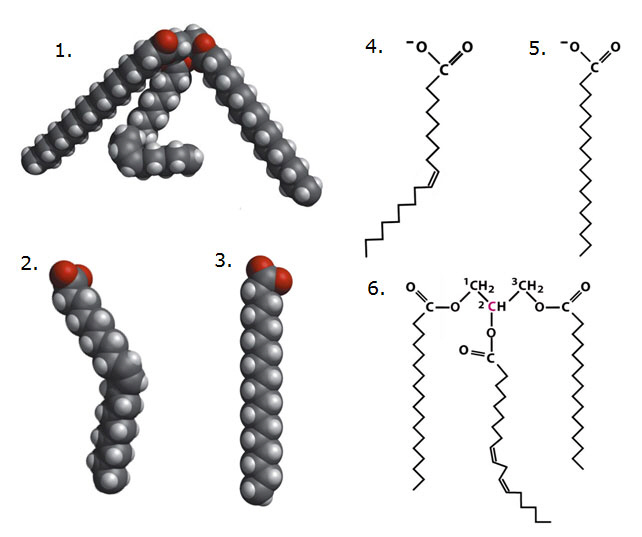
|
|
|
31.
|
Correctly pair the molecules in the diagrams above.
a. | 4.....5 | b. | 1.....4 and 5 | c. | 2.....4 | d. | 3.....5 | e. | both c and d are
correctly paired |
|
|
|
Figure 2: Molecules Essential for Life 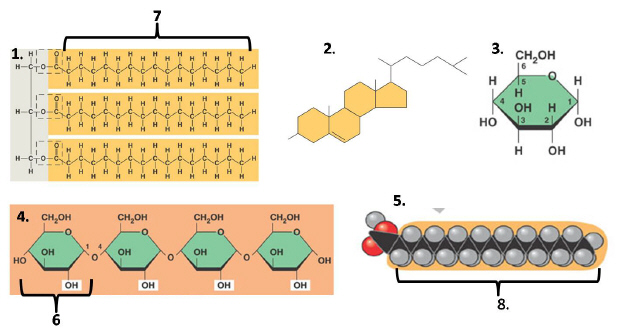
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following diagrams are correctly linked in the answers
below:
a. | 1, 2, 5 are all members of the macromolecules group known as
lipids | b. | 2, 3, 4 are all members of the carbohydrate macromolecule group | c. | 4 and 5 are members
of the protein macromolecule group | d. | 3, 4, and 5 are members of the lipid
macromolecule group | e. | none of the above are completely
correct |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following correctly compares the structure to one of its common
functions.
a. | 1-insulation | b. | 2- stabilization of the cell
membrane | c. | 3- energy molecule | d. | 4.- energy storage in
plants | e. | 5- part of membrane construction | f. | all of the above are
correct | g. | some of the above are correct | h. | all of the above are
incorrect |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following is correctly pairs the possible monomer unit (or
monomer-like unit) to the polymer (or polymer-like unit)?
a. | 7 is the monomer unit to 2 | b. | 2 is the monomer unit to 7 | c. | 3 is the monomer
unit of 4 | d. | 5 is monomer-like unit of 1 | e. | both c and d are
true |
|
|
|
Figure 3- Protein Structure 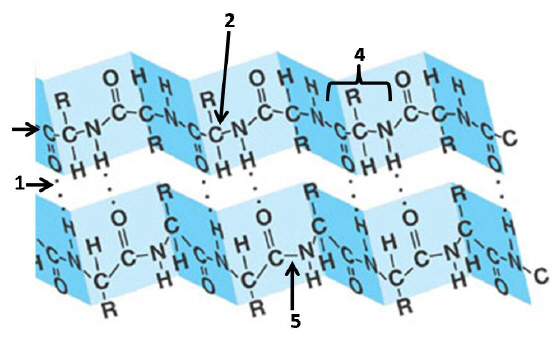
|
|
|
35.
|
The above diagram is showing
a. | secondary structure in a protein | d. | quarternary structure in a
protein | b. | a beta sheet in a protein | e. | backbone interactions of a polypeptide | c. | tertiary interactions in a
protein | f. | a, b, e, are
correct |
|
|
|
Figure 4 Protein Structure
|
|
|
36.
|
The image shown above shows a specific level of protein structure.
a. | The image shows primary level of protein structure through the entire
protein | b. | The image shows three alpha helixes and two beta sheets within the
protein | c. | The image shows tertiary level of structure by showing sidechain
interactions | d. | The image shows quarternary level of structure. There are several polypeptide chains
visible. | e. | both c and d are correct |
|
|
|
Figure 5-Lysosyme 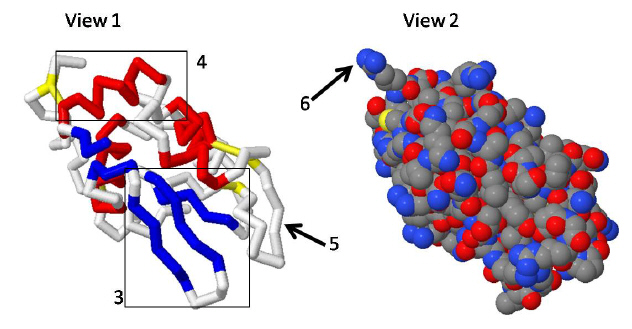
|
|
|
37.
|
The above views of the protein Lyzozyme shows the protein in two different ways.
Which statement best explains the differences within the views.
a. | View 1 shows the details of the primary sequence of the protein whereas View 2 only
shows the backbone of the polypeptide | b. | View 1 and 2 are showing the exact same
information | c. | View 1 shows the secondary structure of a protein whereas view 2 shows the globular,
spacefill view of the protein. | d. | View 1 shows the sidechains that are in the
active site of the protein whereas view 2 shows only tertiary and structure | e. | all of the above are
correct |
|
|
|
38.
|
Using the lyzozyme image above compare the areas highlight by 3 and 4. Which
statement is correct?
a. | the sidechains of area 4 are forming the structural motif known as the
beta-sheet. | b. | the backbone interations of area 4 are forming the structural motif knows as the beta
sheet | c. | The red area highlighted in 4 shows a Beta sheet | d. | the backbone
interactions of area 4 are forming the structural motif knowns as the alpha-helix | e. | the sidechain
interactions of area 4 are forming the structureal motif known as the beta- sheet.
|
|
|
|
39.
|
Areas highlighted by 3 and 4 ---.
a. | are examples of secondary structure | b. | are examples of tertiary
structure | c. | are examples of quarternary sturcture | d. | are examples of primary
structure | e. | both a and d are correct |
|
|
|
40.
|
Compare the information conveyed through the are labeled 5 and the area labeled
6.
Which of the following statements are correct?
a. | Area 6 shows a sidechain | b. | Area 5 shows several
sidechains | c. | Area 6 shows only backbone | d. | Area 5 shows only backbone | e. | a and d are
correct |
|