Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be
a. | GCCTAG. | b. | GCCAUC. | c. | GCCATG. | d. | TAACGT. | e. | CGGTAC. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA is called
a. | a translation. | b. | a mutation. | c. | a
codon. | d. | an advantage. | e. | an anticodon. |
|
|
|
3.
|
The term gene expression refers to the
a. | fact that each individual of a species has a unique set of genes. | b. | process by which
genetic information flows from genes to proteins. | c. | fact that certain genes are visible as dark
stripes on a chromosome. | d. | fact that individuals of the same species have
different phenotypes. | e. | flow of information from parent to
offspring. |
|
|
|
4.
|
The coding regions of a gene (the portions that are expressed as polypeptide
sequences) are called
a. | introns. | b. | nucleosomes. | c. | proto-oncogenes. | d. | redundant coding sections. | e. | exons. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The polymerase chain reaction relies upon unusual, heat-resistant __________
that were isolated from bacteria living in hot springs.
a. | mRNA | b. | phages | c. | plasmids | d. | restriction enzymes | e. | DNA polymerase
molecules |
|
|
|
Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
|
|
|
6.
|
The entire process represented here can be called:
a. | gene expression. | b. | gene regulation. | c. | DNA
replication. | d. | DNA mutation. | e. | Transformation. |
|
|
|
7.
|
This molecule is made of amino acids.
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | Both (1) and (2) | e. | Both (2) and
(3) |
|
|
|
8.
|
The flow of genetic information in a cell can be primarily described as
DNA®RNA®Protein. Which of the following combinations represents this
pathway?
a. | 1, 2, 3 | b. | 1, 4, 2 | c. | 2, 5,
3 | d. | 3, 2, 1 | e. | 1, 1, 2 |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows a molecule of DNA. The labels 1 through 4
point at different parts and characteristics of the molecule. Answer the following questions
based on the diagram.
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following statements is false regarding the diagram?
a. | “1” are covalent bonds that hold the adjacent DNA strands
together. | b. | “2” is the 3’ end of DNA. | c. | “4” is
the “end” where new nucleotides would be added by DNA polymerase. | d. | Both (a) and (c) are
false. | e. | All statements are false. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The DNA monomer unit, labeled “3”, consists of the following:
a. | Phosphate group, deoxyribose, nitrogenous base. | b. | Phosphate group,
ribose, nitrogenous base. | c. | Phosphate group, three fatty
acids. | d. | Phosphate group, glucose, Adenine | e. | Deoxyribose, glucose, nitrogenous
base. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following concepts are not used to describe the characteristics
and/or functions of this molecule?
a. | sidechain | b. | antiparallel | c. | complementary
bases | d. | double stranded | e. | negatively
charged |
|
|
|
The following diagram represents the Lac operon in two different
environments. Answer the following questions based on this diagram.
|
|
|
12.
|
The repressor protein can bind:
a. | 3 and 2 | b. | 5 and 6 | c. | 4 and
9 | d. | 5 and 9 | e. | 6 and 9 |
|
|
|
13.
|
The molecule labeled (8) is:
a. | Lactose | b. | Ribosome | c. | Helicase | d. | DNA polymerase | e. | RNA
polymerase |
|
|
|
14.
|
The molecules labeled (10) are used by the bacteria to:
a. | Break down lactose to generate ATP through cellular respiration. | b. | Bind the operator to
inhibit transcription. | c. | Activate RNA polymerase by breaking down the
repressor molecule. | d. | Begin DNA replication. | e. | Create additional
sugars for the bacteria. |
|
|
|
The following plasmid map shows the three genes on the plasmid pBIO. The
GFP gene and ampicillin resistance gene ( AMPR) are regulated by a promoter
that is always “on”. Therefore, the genes are always expressed once in a
cell. The kanamycin resistance gene ( KANR) is regulated by the Lac
operon. Kanamycin is another antibiotic that prevents the grow of bacteria. Plates
labeled with “Amp” and “Kan” contain the corresponding antibiotics. The
plate labeled with “lactose” contains the sugar lactose. A bacterial culture is
transformed with pBIO and successfully transformed cells are plated on all four plates shown
below. Answer the questions based on your understanding of transformation, regulation by the
Lac operon, and gene expression.
|
|
|
15.
|
You transform bacteria (E.coli) with the plasmid pBIO. The successfully
transformed cells are plated onto the four plates above. On which plate will you not see
any growth?
a. | LB | b. | LB/Amp | c. | LB/Amp/Kan | d. | LB/Amp/Kan/lactose | e. | All plates will have
some growth |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following is not an observation you will make?
a. | The LB plate will show lawn growth because all plated bacteria, including those that
did not take up a plasmid, will be able to grow. | b. | The LB/Amp plate will show colony growth.
Each colony represents a single bacterium that took up the plasmid pBIO and grew into millions of
cells during incubation. | c. | All colonies on the LB/Amp/Kan/Lactose plate
will GLOW because GFP is expressed. | d. | The colonies on the LB/Amp plate will
GLOW. | e. | When untransformed E.coli is plated onto LB/Amp/Kan/lactose, you will see lawn growth
because lactose will help make bacteria resistant to the antibiotics. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is false about the plasmid pBIO?
a. | It is a circular piece of DNA. | b. | It codes for enzymes that make bacteria
resistant to antibiotics. | c. | It codes for enzymes that make the antibiotic
kanamycin. | d. | Contains three genes. | e. | It codes for a gene that makes a protein that
will fluoresce. |
|
|
|
Below is the plasmid map of pAMP. The plasmid has a single ampicillin
resistance gene and an origin of replication. Restriction sites and corresponding nucleotide
numbers are shown. The entire size of pAMP is 4539 base pairs (bp).
The plasmid was cut with the enzymes BamHI and EcoRI. This
reaction produced two fragments with sizes 1120bp and 3419bp.
You accidentally mix up the
digestion reaction with another that you were using for a separate experiment (this is why you should
always label tubes!). Unable to figure out which tube contained your original digestion
reaction, you run samples of both tubes in a gel along with a ladder.
The ladder standards are
DNA fragments with the following sizes: 5000, 4000, 3000, 2000, and 1000.
The diagram to the
right shows the resulting gel. |
|
| |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following statements are true?
a. | Lane 1 contains pAMP digested with BamHI and EcoRI. | b. | Lane 2 contains pAMP
digested with BamHI and EcoRI. | c. | This gel does not provide sufficient
information to identify your pAMP digestion. | d. | Without knowing how much DNA was loaded into
each well in the gel, it is not possible to determine which lane contains your pAMP
digestion. | e. | Both lane 1 and 2 seems to contain the same sample. |
|
|
|
19.
|
You prepare another restriction digestion and digest pAMP with the enzyme
BglI. When you run this DNA sample in a gel, how many bands should you see?
|
|
|
You use PCR to detect for genetically modified corn in food. The diagram
below shows the specific sequences amplified by three different sets of PCR primers. The
following are the sizes of the amplified products of each primer set: CMV 35S = 210, NOS =
200, and PSII = 400. You extract DNA from two food samples (Pingry corn muffin and Veggie
burger). Each sample is used to prepare three separate PCR reactions; each contain one of three
primer sets. Lanes 2 through 4 contain PCR products from the corn muffin. Lanes 5
through 7 contain PCR products from the veggie burger. The three reaction are loaded in the
following order from left to right for each sample: PSII, CMV 35S, NOS. The ladder in lane 1
contain the following DNA fragments (in bp): 1000, 800, 600, 500, 300, 200. 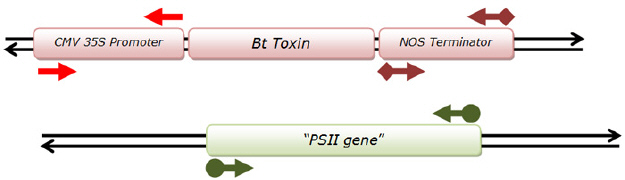
|
|
|
20.
|
Which statement is not consistent with the results of the gel?
a. | The Pingry corn muffin contains genetically modified corn. | b. | The Pingry corn
muffin is engineered using the CMV35S promoter but not the NOS terminator. | c. | The veggie burger is
not genetically engineered. | d. | You were unable to extract DNA from the veggie
burger. | e. | All of the above statements are valid. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Since you don’t see a band in lanes 6 and 7, you suspect that you were
not able to successfully extract DNA from the veggie burger. Your lab partner tells you
that you are wrong. What observation might your lab partner be using to disagree with you?
a. | There is a band in lane 5. | b. | There are bands in lanes 2 and
3. | c. | The band in lane 5 does not correspond with the products of the CMV 35S primer
set. | d. | There are no bands in lanes 6 or 7. | e. | Your lab partner has no idea what he/she is
talking about. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following most accurately describes the necessary components of
the PCR reaction used in this experiment?
a. | Template DNA from food, DNA polymerase, RNA nucleotides | b. | Template DNA from
food, DNA polymerase, DNA nucleotides | c. | Template DNA from food, RNA polymerase, RNA
nucleotides | d. | Template DNA from food, reverse transcriptase, DNA nucleotides | e. | Template DNA from
food, DNA polymerase, ligase, DNA nucleotides |
|
|
|
The following image represents a prokaryotic gene. The highlighted regions
corresponds to different components of the gene including- promoter, coding region, and terminator.
Use the image to answer the following questions.
|
|
|
23.
|
The mRNA transcript will be generated from copying DNA into RNA between which
arrows?
a. | 1 to 7 | b. | 2 to 7 | c. | 3 to
7 | d. | 6 to 4 | e. | 3 to 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.
|
The above image shows a plasmid digest with Ava I enzyme on three
different plasmids.
Which of the following explanation best describes the results observed
from the gel.
a. | Lane 1 shows a plasmid with possibly one cut site | b. | Lane 1 shows a
plasmid with two possible cut sites | c. | Lane 2 shows a digest with two cut
sites | d. | Lane 3 shows a plasmid with three cut sites | e. | All of the above are
correct |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.
|
The plasmids digested above do NOT contain insert. They are plasmids PRIOR to be
ligated to the cDNa insert of duckweed. Draw the possible plasmid maps for each plasmid shown in the
gel image. Plasmid maps require the labeling of the restriction sites.
|