Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Plants need which of the following to carry on photosynthesis?
a. | H2O | b. | CO2 | c. | O2 | d. | lipid | e. | both
H2Oand CO2 |
|
|
|
2.
|
Chlorophyll reflects (does not absorb) which color of light?
a. | red | b. | yellow | c. | orange | d. | green | e. | blue |
|
|
|
3.
|
When light excites chlorophyll, the chlorophyll molecule
a. | changes to carotene. | b. | becomes agitated and moves
rapidly. | c. | becomes radioactive. | d. | absorbs the energy and moves an electron to a
higher energy state. | e. | becomes
ionized. |
|
|
|
4.
|
The correct operational sequence of the three processes listed below is:
| I. |
glycolysis |
| II. |
ETP |
| III. |
Krebs |
| |
a. | I ® II ® III | b. | II ® I ® III | c. | III ® I ®
II | d. | II ® III ® I | e. | I ® III ®
II |
|
|
|
5.
|
Glycolysis depends on a continuous supply of
a. | NADP. | b. | pyruvate. | c. | NAD+. | d. | NADH. | e. | H2O. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Glycolysis
a. | occurs in the mitochondria. | b. | happens to glucose only. | c. | results in the
production of pyruvate. | d. | occurs in the cytoplasm. | e. | results in the
production of pyruvate and occurs in the cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Pyruvate can be regarded as the end product of
a. | glycolysis. | b. | acetyl CoA formation. | c. | fermentation. | d. | the Krebs cycle. | e. | electron
transport. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which is capable of being reduced during both glycolysis and the Krebs
cycle?
a. | NAD+ | b. | FAD+ | c. | ADP | d. | NADH | e. | NADP+ |
|
|
|
9.
|
The Krebs cycle takes place in the
a. | ribosomes. | b. | cytoplasm. | c. | nucleus. | d. | mitochondria. | e. | chloroplasts. |
|
|
|
10.
|
During electron transport phosphorylation, which ions accumulate in the outer
compartment of the mitochondria?
a. | calcium | b. | hydrogen | c. | oxygen | d. | phosphorus | e. | sodium |
|
|
|
11.
|
The ultimate electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is
a. | NAD+ | b. | CO2 | c. | ADP | d. | NADP+ | e. | O2 |
|
|
|
12.
|
The energy used to generate most of the ATP formed in aerobic respiration is
released when electrons ultimately are passed from NADH to which of the following?
a. | oxygen | b. | acetyl CoA | c. | FADH | d. | CO2 | e. | NADPH |
|
|
|
13.
|
The generation of concentration gradients across the membranes of mitochondria
is known as which theory of ATP production?
a. | glycolytic | b. | negative ion generator | c. | phosphate
pump | d. | chemiosmotic | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
14.
|
Under anaerobic conditions muscle cells produce
a. | ethyl alcohol. | b. | acetaldehyde. | c. | pyruvate. | d. | lactate. | e. | citrate. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on the diagram below. 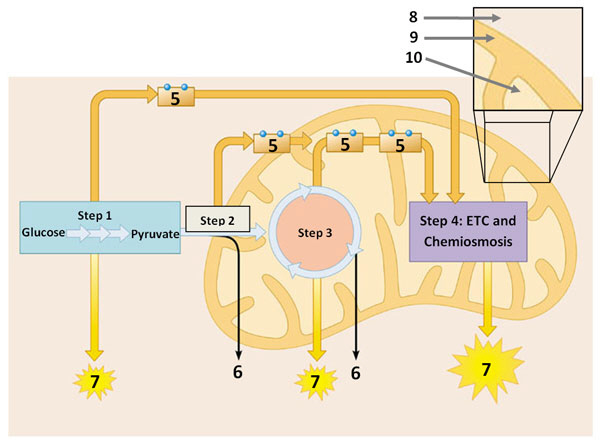
|
|
|
15.
|
The purpose of the pathway/reaction represented in this diagram is:
a. | to convert glucose into more complex macromolecules necessary in the cell including
proteins and lipids. | b. | to use glucose as an energy source to produce
ATP when oxygen is not available in the cell. | c. | to convert light energy into chemical
energy. | d. | to create energy by converting one molecule into another. | e. | to break down high
energy bonds in “food” molecules such as glucose and transfer the energy into molecules
that can be used by the rest of the cell. |
|
|
|
16.
|
The molecules labeled (5):
a. | represent NADH and/or FADH2. | b. | give up high-energy
electrons to the electron transport chain. | c. | release individual carbon atoms in food
molecules as carbon dioxide. | d. | both (a) and (b) above. | e. | all of the
above. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | ATP synthase and the proteins involved in the ETC are found in the membrane between
the spaces labeled (9) and (10). | b. | Hydrogen ions can freely move between the
spaces labeled (8) and (9). | c. | By the end of Step 2, all carbon atoms in
glucose are broken down into carbon dioxide. | d. | (6) represents oxygen. | e. | Step 3 is the Calvin
cycle. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Step 1 is glycolysis. | b. | Step 2 is pyruvate
oxidation. | c. | The carbon dioxide released through this reaction is eventually breathed out of the
body. | d. | This entire reaction (Steps 1 through 4) is all taking place in the
mitochondria. | e. | Per glucose, the most ATP is produced in Step 4. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on the diagram below:
|
|
|
19.
|
Which letter represents a molecule that provides the energy required to
establish a high concentration of ions in the intermembrane space?
|
|
|
20.
|
Without this molecule, the cell will be forced to switch ATP production to
anaerobic respiration.
|
|
|
21.
|
The membrane seen in this diagram is the:
a. | Cell membrane. | b. | Thylakoid membrane. | c. | Nuclear
membrane. | d. | Outer mitochondrial membrane. | e. | Inner mitochondrial
membrane. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on the diagram below:
|
|
|
22.
|
The above diagram shows a pathway that occurs when:
a. | fats are broken down to make ATP. | b. | oxygen is available to the
cell. | c. | oxygen is deficient in the cell. | d. | carbon dioxide is not
available. | e. | more ATP than what is produced through aerobic respiration is
needed. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which statement regarding this diagram is true?
a. | One of the primary purposes of the shown pathway is to regenerate
NAD+. | b. | This process occurs in the mitochondria. | c. | This process only
occurs in plant cell. | d. | This reaction is far more efficient than the
process of ATP production occurring in the mitochondria. | e. | This process can
occur indefinitely in the cell. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on the diagram below:
|
|
|
24.
|
When excess food is consumed:
a. | all macromolecules are broken down in order to form ATP. | b. | all macromolecules
are converted into glucose in order to go through cellular respiration | c. | cellular respiration
is balanced with the storage of excess macromolecules as glycogen, lipids, or other energy-rich
molecules. | d. | the excess food is not
digested. | e. | All above statements are true. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Fatty acids contain many covalently bonded carbons. | b. | Fats can release
more energy when being broken down into intermediates used in cellular
respiration. | c. | Excess glucose can be stored for later use in the form of
glycogen. | d. | The breakdown of fats and proteins require additional enzymes than those involved in
glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. | e. | All reactions shown in this diagram is a
one-way pathway; molecules are only broken down in our cells to produce ATP and these pathways are
not related to how molecules are produced in the cell. |
|
|
|
26.
|
When fats are used for aerobic respiration, enzymes first hydrolyze them
into
a. | glycerol and amino acids. | b. | fatty acids and sugars. | c. | sugars and amino
acids. | d. | glycerol and fatty acids. | e. | sugars and
glycerol. |
|
|
|
Answer the questions based on your understanding of the following diagram.
|
|
|
27.
|
The reaction represented above takes place where in a cell?
a. | The mitochondria. | b. | The nucleus. | c. | The endoplasmic
reticulum. | d. | The matrix. | e. | The
Chloroplast. |
|
|
|
28.
|
This molecule is "fixed" and eventually used to generate glucose,
which can be then used for the synthesis of more complex carbohydrates and other organic
molecules.
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 5 | e. | Both (1) and (3) are
molecules that are “fixed”. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which description best summarizes the purpose of the reaction represented by the
diagram?
a. | Energy stored in large macromolecules such as glucose is released for use in the
cell. | b. | Monomers such as glucose are combined into larger molecules for storage in the
cell. | c. | ATP is produced in the cell to drive biological reactions. | d. | Solar energy is
converted into chemical energy to synthesize carbohydrates. | e. | All of the above
takes place in the reaction represented in the diagram. |
|
|
|
30.
|
This molecule is released as a byproduct of the light-dependent reactions and is
a molecule necessary to generate ATP by metabolizing glucose when light is not available:
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 5. | e. | None of the
above. |
|