Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
The following four diagrams show the structures of different molecules.
Answer the following questions based on your ability to identify them.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which macromolecule is best associated with the terms saturated and
unsaturated?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | All molecules have
saturated and unsaturated structures. |
|
|
|
2.
|
in diagram 4, the “R” represents the:
a. | amino group. | b. | carboxyl group. | c. | enzyme. | d. | active site. | e. | sidechain. |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows a sequence of a reaction. The numbers 1through
4 identify different parts of the overall structure.
|
|
|
3.
|
This reaction is facilitated by which structure in the cell?
a. | DNA polymerase | b. | RNA polymerase | c. | Ribosome | d. | Nucleus | e. | Hydrolase |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows the different levels of structure for a type of
macromolecule. Answer the questions based on your understanding of how these structures are
maintained.
|
|
|
4.
|
Which diagram above, 1-5, represents an alpha-helix, a type of secondary
structure?
|
|
|
5.
|
Which image represents the interaction of multiple polypeptides to form a
functional protein?
|
|
|
Identify the diagram below and answer the following questions.
|
|
|
6.
|
This molecule is a _____, which belongs to the _____ group of
macromolecules.
a. | amino acid... protein. | b. | phospholipid...
polysaccharide. | c. | phospholipid... lipid. | d. | monomer... polymer. | e. | monosaccharide...
polysaccharide. |
|
|
|
7.
|
“The predicted nature of the labeled area _____ is _____ due to
_____.” Which of the following accurately complete this statement?
a. | 1... polar... due to the large phosphate group with multiple oxygen
atoms. | b. | 2... nonpolar... the large number of C-H bonds that tend to share electrons
evenly. | c. | 4... hydrophilic... double bonds within the fatty acid tail. | d. | Both (a) and
(b) | e. | All of the above. |
|
|
|
The two images below both show the structure of the cell membrane composed of
two layers of phospholipids. Recall the chemical characteristics of a phospholipid and its role
in the function of the membrane. The labels (numbers 1 through 5) for the two diagrams
correspond to the same “part” of the two diagrams.
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the labeled regions identifies a single phospholipid molecule?
|
|
|
9.
|
What are you actually referring to when using the term “lipid
bilayer”?
|
|
|
The diagram below shows a transmembrane protein (a protein embedded in the lipid
bilayer) that acts as a channel to transport molecules across the membrane. You should recognize the
parts of the lipid bilayer by comparing them to an earlier question which shows the membrane in the
same view. The boxed area highlights details of the protein chain that sits in the
membrane. Each “R” represents a separate sidechain and is labeled 1 through
5. Answer the following questions based on your understanding of the structure and
characteristics of amino acids, proteins, and the lipid bilayer.
|
|
|
10.
|
This protein exhibits secondary structure characteristics called:
a. | backbones. | b. | hydrophilic. | c. | beta
sheets. | d. | alpha helices. | e. | disulfide
bonds. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The sidechains labeled 4 and 5 can possibly belong to which of the following
amino acids?
a. | Aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and valine. | b. | Alanine, glycine,
and proline. | c. | Asparagine, glutamine, and threonine. | d. | Both (a) and (b) above. | e. | None of the
above. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following statements must be true about the amino acid
sidechain labeled 1?
a. | This sidechain must have similar chemical characteristics to that of fatty acid
chains. | b. | This sidechain must be able to interact with nonpolar molecules. | c. | This sidechain must
be able to interact with water. | d. | Both (a) and (b) above can be
true. | e. | Both (a) and (c) above can be true. |
|
|
|
Protein Structure: Using the following diagram correctly answer the following
questions. 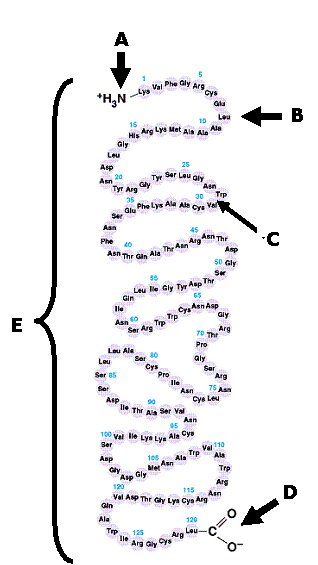
|
|
|
13.
|
The diagram above is a representation of a(an)
a. | amino acid | b. | polypeptide | c. | primary level of
structure of a protein | d. | sidechains | e. | both b. and c.
|
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the labeled areas best identifies the amino terminus of the
protein
|
|
|
15.
|
The region labeled C is best (or most specifically) described as
a. | an R group or side chain | b. | a covalent bond between two amino
acids | c. | a beta sheet | d. | a secondary structure | e. | a tertiary
interaction |
|
|
|
Using diagrams below answer the following questions. 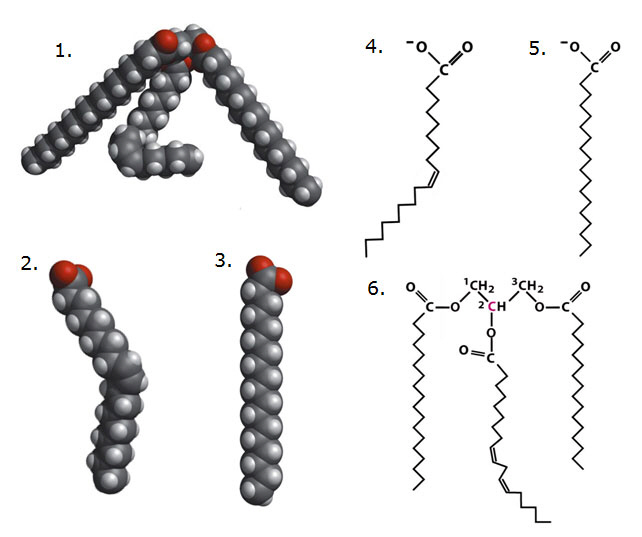
|
|
|
16.
|
Correctly pair the molecules in the diagrams above.
a. | 4.....5 | b. | 1.....4 and 5 | c. | 2.....4 | d. | 3.....5 | e. | both c and d are
correctly paired |
|
|
|
17.
|
Using the diagrams above correctly identify a trigyceride.
a. | 1 and 6 are both trigyclerides | b. | 1 is a phospholipid | c. | 6 is
phospholipid | d. | 4 is a triglyceride | e. | 3 is a
triglyceride |
|
|
|
Using the diagram answer the following questions. 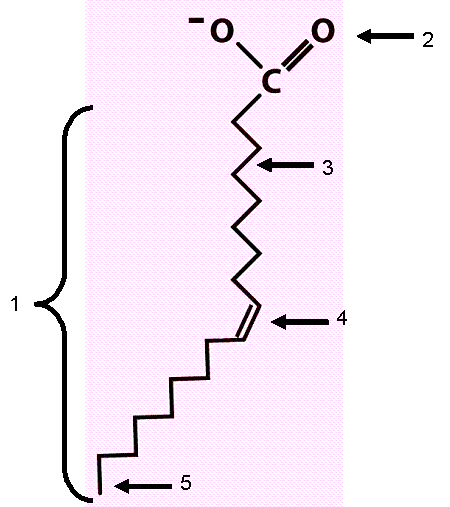
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following correctly matches the chemical nature with the
identified regions?
a. | 2.....polar | b. | 3.....charged | c. | 4.....rotational | d. | 1..... hydrophilic | e. | all of the above are
correctly matched areas |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which end of the molecule will be reactive when considering dehydration
synthesis of a triglyceride?
a. | 1 | b. | 3 | c. | 4 | d. | 2 or 5 | e. | none of the above
regions are involved in a dehydration synthesis reaction |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following terms best describes this molecule?
a. | fatty acid | b. | saturated fatty acid | c. | polypeptide | d. | phospholipid | e. | triglyceride |
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the identified parts corresponds to glycolipid?
|
|
|
Figure 2: Molecules Essential for Life 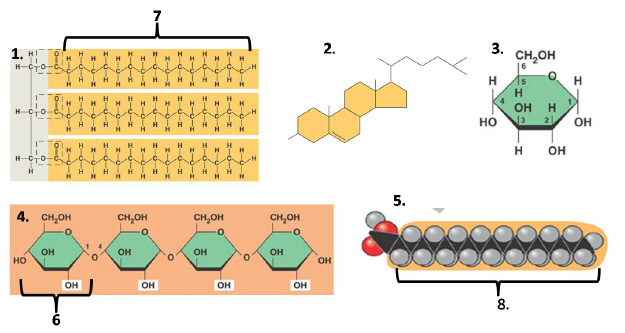
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following diagrams are correctly linked in the answers
below:
a. | 1, 2, 5 are all members of the macromolecules group known as
lipids | b. | 2, 3, 4 are all members of the carbohydrate macromolecule group | c. | 4 and 5 are members
of the protein macromolecule group | d. | 3, 4, and 5 are members of the lipid
macromolecule group | e. | none of the above are completely
correct |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following is correctly pairs the possible monomer unit (or
monomer-like unit) to the polymer (or polymer-like unit)?
a. | 7 is the monomer unit to 2 | b. | 2 is the monomer unit to 7 | c. | 3 is the monomer
unit of 4 | d. | 5 is monomer-like unit of 1 | e. | both c and d are
true |
|
|
|
Figure 3- Protein Structure 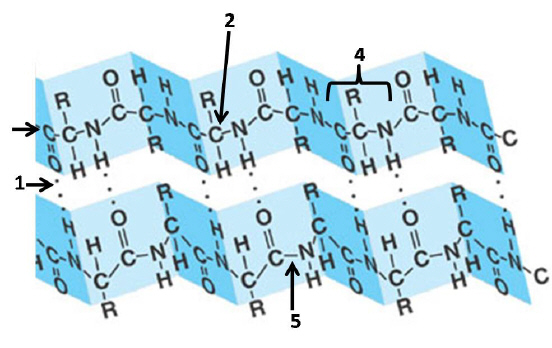
|
|
|
24.
|
The above diagram is showing
a. | secondary structure in a protein | d. | quarternary structure in a
protein | b. | a beta sheet in a protein | e. | backbone interactions of a polypeptide | c. | tertiary interactions in a
protein | f. | a, b, e, are
correct |
|
|
|
Figure 5-Lysosyme 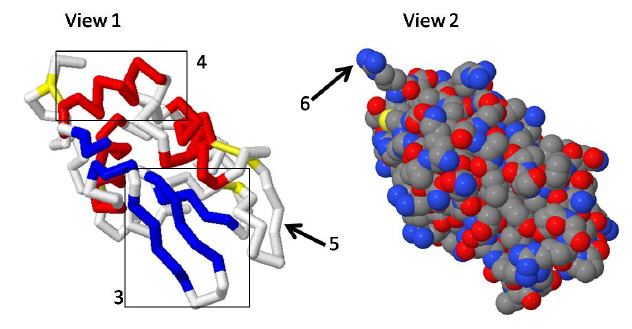
|
|
|
25.
|
Using the lyzozyme image above compare the areas highlight by 3 and 4. Which
statement is correct?
a. | the sidechains of area 4 are forming the structural motif known as the
beta-sheet. | b. | the backbone interations of area 4 are forming the structural motif knows as the beta
sheet | c. | The red area highlighted in 4 shows a Beta sheet | d. | the backbone
interactions of area 4 are forming the structural motif knowns as the alpha-helix | e. | the sidechain
interactions of area 4 are forming the structureal motif known as the beta- sheet.
|
|
|
|
Observe the following image carefully and answer the following
questions. 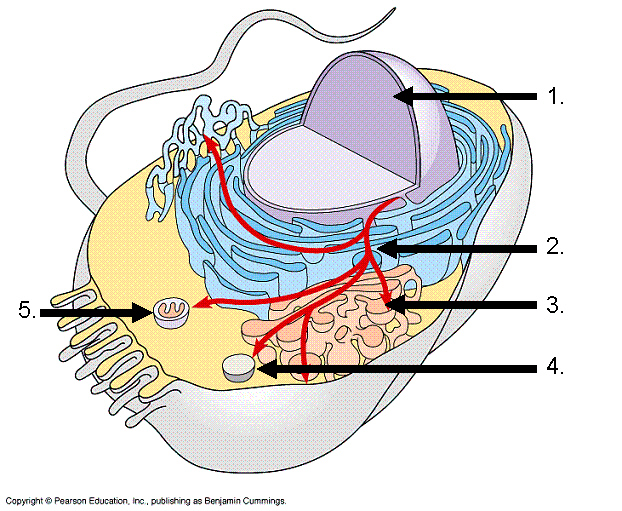
|
|
|
26.
|
The cell in the above diagram is very clearly a eurkaryotic cell. Choose below
the answer the cites the evidence for this claim
a. | the presence of cytoplasm which is highlighted by #5. | b. | The presence of cell
membrane | c. | the presence of nucleus (1), rough ER (2), and golgi apparatus
(3) | d. | the presence of a flagella | e. | the prssence of a
mitochondria |
|
|
|
Observe the following image carefully and answer the following
questions.
|
|
|
27.
|
The image above is a example of a --- cell, which is a --- type of cell.
a. | plant cell........prokaryotic | b. | animal......eukaryotic | c. | plant........eukaryotic | d. | bacteria......viral | e. | walled........rotational |
|
|
|
Observe the following diagram and answer the following
questions. 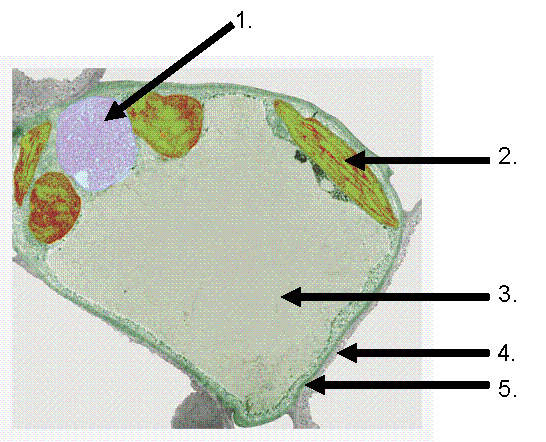
|
|
|
28.
|
Which structure(s) identified above is (are) unique only to plant cells?
a. | 1 | b. | 1.....2 | c. | 1.....2.....3 | d. | 2.....3.....4 | e. | 1.....2.....3.....4.....5. |
|
|
|
29.
|
The structure labeled (3) is specifically involved in---.
a. | protein synthesis | b. | harvesting sunlight and converting it to
chemical energy | c. | storage of pigments and starch | d. | storage of genetic material | e. | all of the above are
possible in this structure |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the above labeled structures (is) are constructed from a structural
polysacharride?
a. | 1 | b. | 1 and 2 | c. | 2 and
3 | d. | 4 | e. | 3 and 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.
|
Using the above diagram which of the following choices are unique only to
eukaryotic cells
a. | 1 and 2 | b. | 1 and 2 and 3 | c. | 1 and 4 and
5 | d. | 4 and 5 | e. | 5 |
|
|
|
32.
|
You now know that the old cliche "oil and water don't mix" is
true. Why?
a. | Water exhibits polarity and oil does not. | b. | Oil exhibits
polarity and water does not. | c. | Oil is an organic compound and water is
not. | d. | Oil is hydrophilic. | e. | Water is
hydrophobic. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which list below consists of only polymers?
a. | sugars, amino acids, nucleic acids, lipids | b. | proteins, lipids,
nucleic acids, polysaccharides | c. | proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, amino
acids | d. | polysaccharides, lipids, amino acids, nucleic acids | e. | proteins, lipids,
nucleotides, sugars |
|
|
|
34.
|
The molecular formula of most monosaccharides represents a multiple of
a. | CH3O. | b. | CHO. | c. | CHO2. | d. | CH2O. | e. | CHO3. |
|
|
|
35.
|
The storage form of carbohydrates in animals is __________ and in plants is
__________.
a. | glycogen . . . starch | b. | starch . . . glycogen | c. | sucrose . . .
glycogen | d. | cellulose . . . glycogen | e. | glycogen . . .
cellulose |
|
|
|
36.
|
Nucleotides
a. | contain nitrogenous bases. | b. | contain phosphate groups. | c. | contain sugar
molecules. | d. | can be linked together to form nucleic acids. | e. | All of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
37.
|
A new "wonder food" is being distributed by a rival company. The
researchers in your company determine that the "wonder food" contains only carbon, oxygen,
and hydrogen. At this point, your researchers can say with certainty that the food
a. | could only be made of carbohydrates. | b. | includes proteins. | c. | could only be made
of triglycerides. | d. | does not include proteins or nucleic
acids. | e. | includes nucleic acids. |
|
|
|
38.
|
As cell size increases, the
a. | volume and surface area decrease. | b. | surface area increases faster than the
volume. | c. | volume increases faster than the surface area. | d. | surface area and
volume increase at the same rate. | e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
39.
|
You are told that the cells on a microscope slide are plant, animal, or
bacterial. You look at them through a microscope and see cell walls and membrane-bound organelles.
You conclude that the cells
a. | could be either plant or bacterial. | b. | could be plant, animal, or
bacterial. | c. | are animal cells. | d. | are plant cells. | e. | are
bacteria. |
|
|
|
40.
|
The cells that produce hair contain a lot of __________. The cells that
produce the oils that coat the hair contain a lot of __________.
a. | nuclei . . . chromatin | b. | smooth endoplasmic reticulum . . .
lysosomes | c. | microbodies . . . lysosomes | d. | smooth endoplasmic reticulum . . . rough
endoplasmic reticulum | e. | rough endoplasmic reticulum . . . smooth
endoplasmic reticulum |
|