Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Through meiosis
a. | alternate forms of genes are shuffled. | b. | parental DNA is divided and distributed to
forming gametes. | c. | the diploid chromosome number is reduced to haploid. | d. | offspring are
provided with new gene combinations. | e. | all of these |
|
|
|
2.
|
If a parent cell has 16 chromosomes and undergoes meiosis, the resulting cells
will have how many chromosomes?
|
|
|
3.
|
Homologous chromosomes
a. | may exchange parts during meiosis. | b. | have alleles for the same characteristics even
though the gene expression may not be
the same. | c. | are in pairs, one
chromosome of each pair from the father and one from the mother. | d. | pair up during
meiosis. | e. | all of these |
|
|
|
4.
|
Copies of chromosomes linked together at their centromeres at the beginning of
meiosis are appropriately called what kind of chromatids?
a. | mother | b. | daughter | c. | sister | d. | homologous | e. | none of
these |
|
|
|
5.
|
Meiosis typically results in the production of
a. | 2 diploid cells. | b. | 4 diploid cells. | c. | 4 haploid
cells. | d. | 2 haploid cells. | e. | 1 triploid
cell. |
|
|
|
6.
|
A locus is
a. | a recessive gene. | b. | an unmatched allele. | c. | a sex
chromosome. | d. | the location of an allele on a chromosome. | e. | a dominant
gene. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Diploid organisms
a. | have corresponding alleles on homologous chromosomes. | b. | are usually the
result of the fusion of two haploid gametes. | c. | have two sets of
chromosomes. | d. | have pairs of homologous chromosomes. | e. | all of these |
|
|
|
8.
|
If R is dominant to r, the offspring of the cross of RR
with rr will
a. | be homozygous. | b. | display the same phenotype as the RR
parent. | c. | display the same phenotype as the rr parent. | d. | have the same
genotype as the RR parent. | e. | have the same genotype as the rr
parent. |
|
|
|
9.
|
The F2 phenotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross is
a. | 1:1. | b. | 2:1. | c. | 9:3:3:1. | d. | 1:2:1. | e. | 3:1. |
|
|
|
10.
|
If all offspring of a cross have the genotype Aa, the parents of the
crosses would most likely be
a. | AA x aa. | b. | Aa x Aa. | c. | Aa x
aa. | d. | AA x Aa. | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
11.
|
Some dogs have erect ears; others have drooping ears. Some dogs bark when
following a scent; others are silent. Erect ears and barking are due to dominant alleles located on
different chromosomes. A dog homozygous for both dominant traits is mated to a droopy-eared, silent
follower. The phenotypic ratio expected in the F1 generation is
a. | 9:3:3:1. | b. | 100 percent of one
phenotype. | c. | 1:1. | d. | 1:2:1. | e. | none of
these |
|
|
|
12.
|
Individuals with the genotype Gg Hh Ii Jj will produce how many different
kinds of gametes?
|
|
|
13.
|
In cocker spaniels, black coat color (B) is dominant over red (b),
and solid color (S) is dominant over spotted (s). If a red male was crossed with a
black female to produce a red spotted puppy, the genotypes of the parents (with male genotype first)
would be
a. | Bb Ss x Bb Ss. | b. | bb Ss x Bb
Ss. | c. | bb ss x Bb Ss. | d. | bb Ss x Bb
ss. | e. | Bb ss x Bb ss. |
|
|
|
14.
|
In cocker spaniels, black coat color (B) is dominant over red (b),
and solid color (S) is dominant over spotted (s). A cross of Bb Ss with bb
ss would produce the phenotypic ratio
a. | 9:3:3:1. | b. | 1:1:1:1. | c. | 1:2:1. | d. | 3:1. | e. | none of
these |
|
|
|
15.
|
An incompletely dominant gene controls the color of chickens so that BB
produces black, Bb produces a slate-gray color called blue, and bb produces splashed
white. A second gene controls comb shape, with the dominant gene R producing a rose comb and
r producing a single comb. If a pure-breeding black chicken with a rose comb is mated to a
splashed white chicken with a single comb in the F2 generation, what fraction of
the offspring will be black with rose comb?
a. | 9/16 | b. | 3/8 | c. | 3/16 | d. | 1/8 | e. | 1/16 |
|
|
|
16.
|
If red (RR) is crossed with white (rr) and produces a pink flower
(Rr), and tall (D) is dominant to dwarf (d), the F2 phenotypic
ratio from a cross of RR dd with rr DD would be
a. | 9:3:3:1. | b. | 1:1:1:1. | c. | 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1. | d. | 3:6:3:1:2:1. | e. | none of
these |
|
|
|
17.
|
Susan, a mother with type B blood, has a child with type O blood. She claims
that Craig, who has type A blood, is the father. He claims that he cannot possibly be the father.
Further blood tests ordered by the judge reveal that Craig is AA. The judge rules that
a. | Susan is right and Craig must pay child support. | b. | Craig is right and
doesn't have to pay child support. | c. | Susan cannot be the real mother of the child;
there must have been an error made at the hospital. | d. | it is impossible to reach a decision based on
the limited data available. | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
18.
|
Multiple effects of a single gene is known as
a. | expressivity. | b. | penetrance. | c. | codominance. | d. | pleiotropy. | e. | multiple
alleles. |
|
|
|
19.
|
All of the genes located on a given chromosome comprise a
a. | karyotype. | b. | bridging cross. | c. | wild-type
allele. | d. | linkage group. | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
20.
|
If the paternal chromosome has alleles L, M, and n and the
maternal chromosomes have l, m, and N, then the chromosome that cannot be
produced by crossing over is
a. | LMN | b. | LMn | c. | LmN | d. | Lmn | e. | lmn |
|
|
|
21.
|
Red-green colorblindness is an X-linked recessive trait in humans. A colorblind
woman and a man with normal vision have a son. What is the probability that the son is
colorblind?
a. | 100 percent | b. | 75 percent | c. | 50
percent | d. | 25 percent | e. | 0 percent |
|
|
|
22.
|
If a daughter expresses an X-linked recessive gene, she inherited the trait
from
a. | her mother. | b. | her father. | c. | both
parents. | d. | neither parent. | e. | her
grandmother. |
|
|
|
23.
|
An X-linked carrier is a
a. | homozygous dominant female. | b. | heterozygous female. | c. | homozygous recessive
female. | d. | homozygous male. | e. | heterozygous
male. |
|
|
|
24.
|
A chromosome's gene sequence that was ABCDEFG before modification and
ABCDLMNOP afterward is an example of
a. | inversion. | b. | deletion. | c. | duplication. | d. | translocation. | e. | crossing
over. |
|
|
|
25.
|
A chromosome's gene sequence that was ABCDEFG before damage and ABFEDCG
after is an example of
a. | inversion. | b. | deletion. | c. | duplication. | d. | translocation. | e. | crossing
over. |
|
|
|
26.
|
The condition occurring when an organism has a 2n + 1 chromosome
composition is known as
a. | monosomy. | b. | trisomy. | c. | diploid. | d. | haploid. | e. | both trisomy and
haploid. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Suppose a hemophilic male (X-linked recessive allele) and a female carrier for
the hemophilic trait have a nonhemophilic daughter with Turner syndrome. Nondisjunction could have
occurred in
a. | both parents. | b. | neither parent. | c. | the father
only. | d. | the mother only. | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
The following graph tracks the amount of DNA in a
single nucleus through the process of meiosis. Answer the questions based on the
graph.
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following statements is
false?
a. | Tetrads form during IV. |
b. | Cells are diploid during IV. |
c. | Cells are diploid during XII. |
d. | DNA is replicated once during this process. |
e. | The cell divides twice during this
process. |
|
|
|
The following pedigree shows the inheritance of an
autosomal genetic disorder inherited in simple Mendelian patterns.
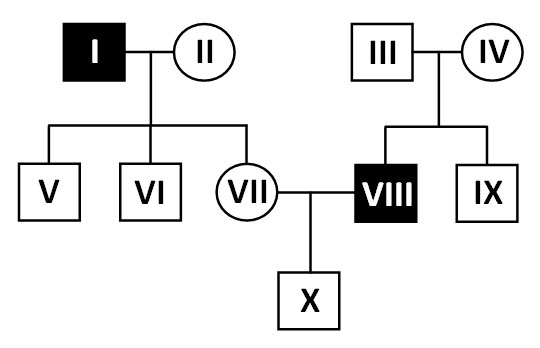
|
|
|
29.
|
Determine if the genetic disorder is dominant or
recessive. Which individual can possibly be a NON-carrier of the allele causing the
disorder.
a. | III |
b. | V |
c. | IX |
d. | X |
e. | All individuals
above must have at least one copy of the affected allele. |
|
|
|
The following pedigree shows the inheritance of an
X-linked recessive disorder.
|
|
|
30.
|
Which individual does not have the recessive
allele?
a. | I |
b. | IV |
c. | V |
d. | IX |
e. | Both V and
IX. |
|