Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A water molecule (H-O-H) is held together by
a. | a single covalent bond. | b. | hydrogen bonds. | c. | a double covalent
bond. | d. | an ionic bond. | e. | a polar covalent
bond. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Glucose dissolves in water because it
a. | ionizes. | b. | is a polysaccharide. | c. | is polar and forms
many hydrogen bonds with the water molecules. | d. | has a very reactive primary
structure. | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
3.
|
A molecule with the formula 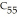 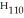 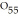 is probably a(n) a. | protein. | b. | oil. | c. | steroid. | d. | polysaccharide. | e. | wax. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which one of the following lists contains only polysaccharides?
a. | sucrose, starch, and cellulose | b. | fructose, cellulose, and
glucose | c. | cellulose, starch, and glycogen | d. | nucleotides, glycogen, and
cellulose | e. | starch, amino acids, and glycogen |
|
|
|
5.
|
Amino acids can be distinguished from one another by
a. | the chemical properties of their amino and carboxyl groups. | b. | the type of bond
between the R group and the rest of the amino acid molecule. | c. | the number of R
groups found on the amino acid molecules. | d. | the chemical properties of their R
groups. | e. | All of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Peptide bonds
a. | link amino acids. | b. | form between fatty acids. | c. | are used to form
amino acids. | d. | are formed by a hydrolysis reaction. | e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The __________ structure of a protein consists of a chain of amino acids
assembled in a specific order.
a. | secondary | b. | tertiary | c. | quaternary | d. | primary | e. | None of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which one of the following is not the proper pairing of a polymer and its
monomer?
a. | protein and amino acid | b. | triglyceride and steroid | c. | nucleic acid and
nucleotide | d. | polysaccharide and monosaccharide | e. | All of the pairs properly reflect a polymer and
its corresponding monomer. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Nucleotides are the building blocks for
a. | proteins. | b. | steroids. | c. | lipids. | d. | ATP, NAD+, and
FAD. | e. | carbohydrates. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Unlike animal cells, plant cells have __________ and __________. Unlike
plant cells, animal cells have __________.
a. | chloroplasts . . . cell walls . . . a nucleus | b. | centrioles . . .
cell walls . . . large central vacuoles | c. | centrioles . . . chloroplasts . . . cell
walls | d. | chloroplasts . . . cell walls . . . centrioles | e. | chloroplasts . . .
cell walls . . . cell membranes |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which one of the following statements is false? The Golgi
apparatus
a. | sorts molecules according to their destination. | b. | works closely with
the endoplasmic reticulum. | c. | modifies chemicals received from the
endoplasmic reticulum. | d. | decreases in size when a cell increases its
protein production. | e. | serves as a molecular warehouse and finishing
factory. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The function of chloroplasts is
a. | intracellular transport of proteins. | b. | cellular respiration. | c. | lipid
synthesis. | d. | intracellular digestion. | e. | photosynthesis. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Mitochondria differ from chloroplasts in that mitochondria
a. | convert solar energy to chemical energy, whereas chloroplasts convert one form of
chemical energy to another. | b. | contain three different membrane-bound
compartments, whereas chloroplasts contain two. | c. | contain membrane folds called cristae, whereas
chloroplasts contain disklike vesicles in stacks called grana. | d. | produce glucose,
whereas chloroplasts break glucose down. | e. | are not found in plants, whereas chloroplasts
are not found in animals. |
|
|
|
14.
|
All cells on Earth
a. | can interconvert forms of energy. | b. | are enclosed in a membrane that maintains
internal conditions different from the surroundings. | c. | can interconvert chemical
materials. | d. | have DNA as the genetic material. | e. | All of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following is NOT true of enzyme behavior?
a. | Enzyme shape may shift during catalysis. | b. | The active site of
an enzyme orients its substrate molecules, thereby promoting interaction of their reactive
parts. | c. | All enzymes have an active site where substrates are temporarily
bound. | d. | Each enzyme can catalyze a wide variety of different reactions. | e. | none of
these |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which affects the rate of diffusion through a semipermeable membrane?
| I. |
steeper concentration
gradients |
| II. |
higher
temperatures |
| III. |
membrane pore size |
| |
a. | I only | b. | II only | c. | I and
II | d. | II and III | e. | I, II, and III |
|
|
|
17.
|
Movement of a molecule against a concentration gradient is
a. | simple diffusion. | b. | facilitated diffusion. | c. | osmosis. | d. | active transport. | e. | passive
transport. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The overall equation for the cellular respiration of glucose is
a. | 5 CO2 + 6 H2O --> C6H12O6 +
6O2 + energy. | b. | C6H12O12 +
3O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy. | c. | C3H12O6 + 6O2 --> 5
CO2 + 6 H2O + energy. | d. | C6H12O6+
6O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy. | e. | None of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Oxidation is the __________, and reduction is the __________.
a. | loss of electrons . . . gain of electrons | b. | gain of electrons .
. . loss of electrons | c. | loss of oxygen . . . gain of
oxygen | d. | gain of protons . . . loss of protons | e. | gain of oxygen . . . loss of
oxygen |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of stages in cellular
respiration?
a. | the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis | b. | oxidative
phosphorylation, the citric acid cycle, and glycolysis | c. | oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis, and the
citric acid cycle | d. | glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and the
citric acid cycle | e. | glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and
oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
|
21.
|
The summary equation for photosynthesis is
a. | the same as the equation for glycolysis written in reverse. | b. | C5H12O6 + 6 O2 + sunlight --> 5
CO2 + 6 H2O. | c. | C6H12O6 + 6
O2 + sunlight --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O. | d. | 6 CO2 + 6
H2O + sunlight ? C6H12O6 + 6
O2. | e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Mitochondria transfer _____ energy from _____ to ATP; chloroplasts transform
_____ energy into the chemical energy of ATP.
a. | food . . . light . . . nuclear | b. | light . . . food . . .
kinetic | c. | food . . . light . . . chemical | d. | chemical . . . food . . .
light | e. | nuclear . . . light . . . food |
|
|
|
23.
|
If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be
a. | CGGTAC. | b. | TAACGT. | c. | GCCAUC. | d. | GCCTAG. | e. | GCCATG. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which one of the following sequences best describes the flow of information when
a gene directs the synthesis of a cellular component?
a. | protein --> RNA --> DNA | b. | DNA --> amino acid --> RNA -->
protein | c. | RNA --> DNA --> RNA --> protein | d. | DNA --> RNA
--> protein | e. | DNA --> tRNA --> mRNA --> protein |
|
|
|
25.
|
We would expect that a 15-nucleotide sequence will direct the production of a
polypeptide that consists of
a. | 7 amino acids. | b. | 3 amino acids. | c. | 5 amino
acids. | d. | 2 amino acids. | e. | 15 amino acids. |
|