Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Lynn Margulis and other biologists believe that
a. | the mitochondrial DNA code was a parallel but more ancient code than nuclear
DNA. | b. | mitochondria were at one time separate, free-living organisms similar to bacteria,
rather than organelles. | c. | mitochondria were obligate symbionts, with both
the mitochondrion and the cell it inhabited benefiting from the relationship. | d. | all of
these | e. | none of these |
|
|
|
2.
|
Eukaryotic cells spend most of their cell cycle in which phase?
a. | anaphase | b. | interphase | c. | prophase | d. | metaphase | e. | telophase |
|
|
|
3.
|
Nondisjunction occurs when
a. | a portion of a chromosome breaks off and is lost. | b. | two chromosomes fuse
into one. | c. | members of a chromosome pair fail to separate. | d. | chromosomes
replicate too many times. | e. | an entire pair of chromosomes is lost during
meiosis I. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which one of the following is false?
a. | The genetic makeup of an organism constitutes its genotype. | b. | The expressed
physical traits of an organism are called its phenotype. | c. | Alleles are
alternate forms of a gene. | d. | An organism with two different alleles for a
single trait is said to be heterozygous. | e. | An allele that is fully expressed is referred
to as recessive. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Alleles of a gene are found at __________ chromosomes.
a. | different loci on heterologous | b. | the same locus on
heterologous | c. | different loci on homologous | d. | the same locus on homologous
mitochondrial | e. | the same locus on homologous |
|
|
|
6.
|
A carrier of a genetic disorder who does not show symptoms is most likely to be
__________ to transmit it to offspring.
a. | homozygous for the trait and unable | b. | homozygous for the trait and
able | c. | heterozygous for the trait and able | d. | heterozygous for the trait and
unable | e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Many genetic disorders of humans are caused by
a. | drinking during pregnancy. | b. | recessive alleles. | c. | a mutation that
occurs in the egg, sperm, or zygote that gives rise to the affected individual. | d. | multiple
alleles. | e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The vast majority of people afflicted with recessive disorders are born to
parents who were
a. | not affected at all by the disease. | b. | subjected to some environmental toxin that
caused the disease in their children. | c. | slightly affected by the disease, showing some
but not all of the symptoms. | d. | both affected by the
disease. | e. | None of the choices are correct. |
|
|
|
9.
|
What is the normal complement of sex chromosomes in a human male?
a. | two Y chromosomes | b. | one Y chromosome | c. | two X
chromosomes and one Y chromosome | d. | two X chromosomes | e. | one X
chromosome and one Y chromosome |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following is/are recessive sex-linked human conditions?
a. | red-green color blindness | b. | hemophilia | c. | muscular
dystrophy | d. | All of the choices are correct. | e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which one of the following is false?
a. | One RNA molecule can include four different nucleotides in its
structure. | b. | RNA is a nucleic acid. | c. | RNA uses the sugar
dextrose. | d. | RNA uses the nitrogenous base uracil. | e. | RNA molecules have a sugar-phosphate
backbone. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which one of the following is false?
a. | DNA molecules have a sugar-phosphate backbone. | b. | DNA uses the sugar
deoxyribose. | c. | DNA uses the nitrogenous base uracil. | d. | DNA is a nucleic acid. | e. | One DNA molecule can
include four different nucleotides in its structure. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which one of the following sequences best describes the flow of information when
a gene directs the synthesis of a cellular component?
a. | DNA ® tRNA ® mRNA ® protein | b. | RNA ® DNA ? RNA
® protein | c. | protein ® RNA ® DNA | d. | DNA ® RNA ®
protein | e. | DNA ® amino acid ® RNA ® protein |
|
|
|
14.
|
The directions for each amino acid in a polypeptide are indicated by a codon
that consists of __________ nucleotide(s) in an RNA molecule.
|
|
|
15.
|
Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA is called
a. | a translation. | b. | a mutation. | c. | a
codon. | d. | an advantage. | e. | an anticodon. |
|
|
|
16.
|
The coding regions of a gene (the portions that are expressed as polypeptide
sequences) are called
a. | introns. | b. | nucleosomes. | c. | proto-oncogenes. | d. | redundant coding sections. | e. | exons. |
|
|
|
17.
|
A population is
a. | a collection of communities. | b. | a group of individuals of different species
living in the same place at the same time. | c. | the smallest unit that can
evolve. | d. | applicable only to animals that reproduce asexually. | e. | All of the choices
are correct. |
|
|
|
18.
|
A change in the relative frequencies of alleles in the gene pool of a population
is called
a. | diversifying selection. | b. | microevolution. | c. | genetic
drift. | d. | directional selection. | e. | mutation. |
|
|
|
19.
|
In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, homozygous dominant individuals in a population
are represented by
a. | 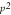 . . | b. | 2pq. | c. | 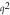 . . | d. | q or p. | e. | None of the choices are
correct. |
|
|
|
20.
|
In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes during G1, each daughter cell
will have how many chromosomes?
|
|
|
21.
|
Cells with two sets of genetic information are described by the term
a. | polyploid. | b. | diploid. | c. | triploid. | d. | haploid. | e. | tetraploid. |
|
|
|
Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
|
|
|
22.
|
The entire process represented here can be called:
a. | gene expression. | b. | gene regulation. | c. | DNA
replication. | d. | DNA mutation. | e. | Transformation. |
|
|
|
The following diagram shows a cross section of a plant root tip. Answer
the questions based on your ability to identify the stage of the cell cycle the cells are in. 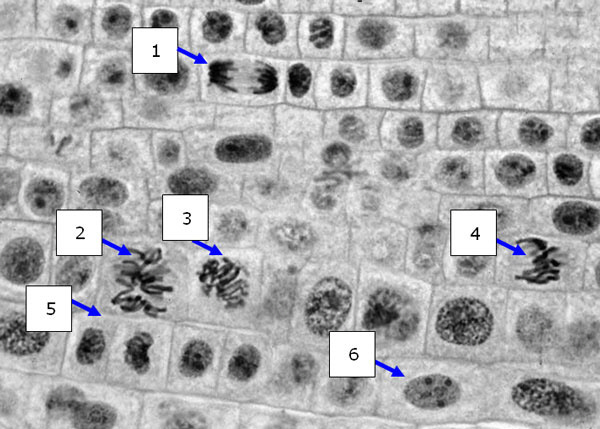
|
|
|
23.
|
Which cell is most likely to be in interphase?
|
|
|
24.
|
Which cell no longer contains DNA organized as sister chromatids?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 4 | e. | All of the
above. |
|
|
|
The next two questions refer to the following diagram. 1, 3, and 5 refer
to the actual structure represented by the diagram. 2 and 4 refer to the event/stage
represented by the arrow.
|
|
|
25.
|
Diagram (3) represents:
a. | centromeres. | b. | chromatin. | c. | a single molecule of
DNA. | d. | two molecules of DNA that are exact copies of each other. | e. | homologous
chromosomes. |
|
|
|
Answer the following questions based on this graph and images: The
following graph was created using data collected through the “Natural Selection” done in
class. The “beans” used to simulate the prey population are diagramed
below.
|
|
|
26.
|
The y axis (left side) represents which of the following?
a. | The allele frequency of the gene affecting “color”. | b. | The frequency of
each “prey” phenotype. | c. | The number of each “prey” phenotype
left in each generation. | d. | The fitness level of each
phenotype. | e. | The effectiveness of each “predator” group to capture the
“prey”. |
|
|
|
The following four diagrams show the structures of different molecules.
Answer the following questions based on your ability to identify them.
|
|
|
27.
|
Which diagram represents the monomer units of proteins?
a. | 1. | b. | 2. | c. | 3. | d. | 4. | e. | Both (2) and
(4) |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which molecule, when broken down into its monomers, is consumed in the
glycolysis pathway?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 4 | e. | Both (2) and
(3) |
|
|
|
Using diagrams below answer the following questions. 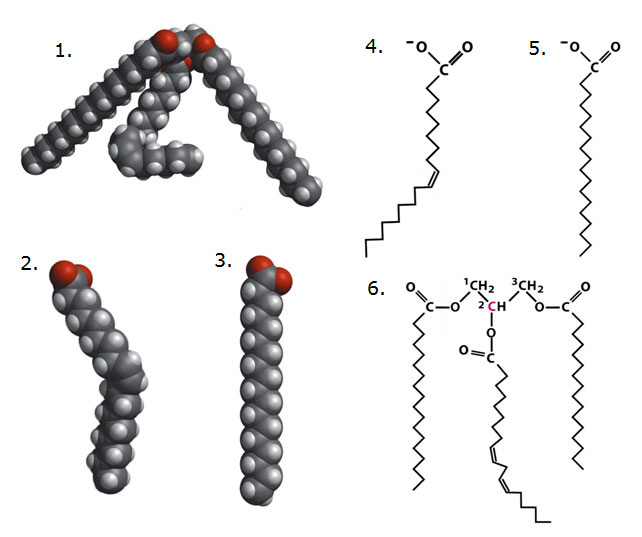
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the above diagrams show an unsaturated fat?
a. | 1, 4, 5, 6 | b. | 2, 3, 1 | c. | 1, 2, 6,
4 | d. | 5, 3, 1 | e. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
Using the diagram answer the following questions. 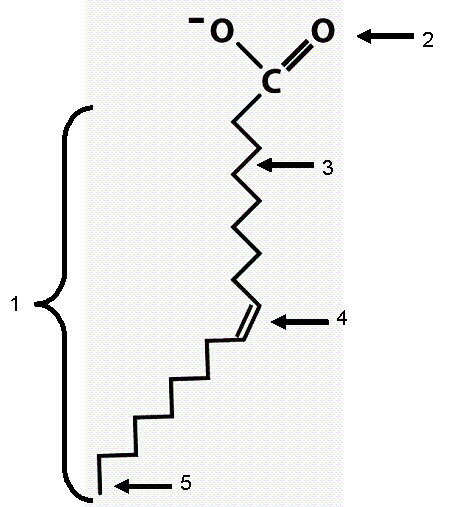
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following terms best describes this molecule?
a. | fatty acid | b. | saturated fatty acid | c. | polypeptide | d. | phospholipid | e. | triglyceride |
|